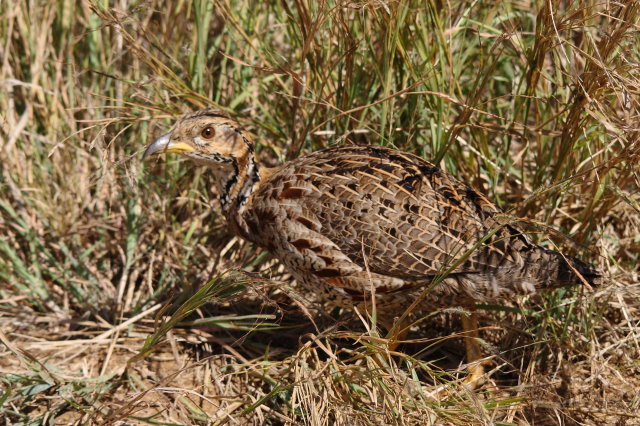
188. Coqui Francolin Peliperdix coqui (Swempie)
Order: Galliformes. Family: Phasianidae
Description
Length 20-28 cm, weight 191-314 g. The Coqui Francolin is arguably the smallest francolins in southern Africa. Bill black with yellow base. Legs yellow.
The adult male is easily distinguished from other francolins by the plane reddish-brown head contrasting with the barred underparts. Ad male: Head plain mustard yellow, crown dark chestnut. Lower neck, mantle and upper breast densely barred black and white. Remainder of upper parts mostly brown, feathers with white to buff central streak and buff transverse barring, together forming criss-cross pattern; some irregularly blotched black. Tail orange-buff, conspicuous in flight but at rest largely obscured by long, barred upper tail coverts. Lower breast and belly pale cream, barred black, bars forming series of chevrons. Bill grey with yellow base. Eyes reddish brown. Legs rich yellow, with moderate tarsal spurs.
Adult female: Has a pale eyebrow with black stripe above and white throat with black border and plain buffy breast.
Juvenile resembles female, but less streaked above.
Similar species: The female can be distinguished from other francolins, Shelley's Francolin in particular, by the white eye stripe and lack of chestnut stripes on breast and flanks.
Distribution
Sub-Saharan Africa: Senegal and southern Ethiopia to north-eastern South Africa.
Habitat
Woodland and savanna; especially those with sandy soils.
Diet
Feeds mainly on above ground food such as seeds, shoots and small fruits. To a lesser extent feeds on underground corms and bulbs, using mainly its bill rather than scratching the soil with its legs as in most other francolins. In the warmer months also feeds in invertebrates.
Breeding
Monogamous. Breeds towards the end of the rainy season or early in the dry season when grass is long and unburnt and seed supply is hence at a peak. Egg-laying season is almost year-round, peaking from December-May. Lays clutch of 3-6 whitish eggs, incubation period unknown, only the female incubates the eggs. The chick can fly after 7-10 days.
Call
High pitched 2-syllable co-qui, co-qui. Dominant call by male is ter, ink, ink, terra, terra, terra. Listen to Bird Call.
Status
Common resident. Widespread but with patchy distribution and locally common only in isolated areas.
Africa Wild Bird Book
Coqui Francolin Photos
188. Coqui Francolin Peliperdix coqui
 © lowveldboy
© lowveldboy
Male
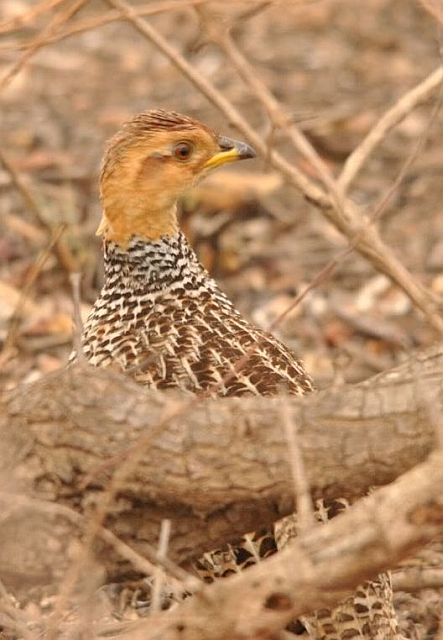
 © Dewi
© Dewi
Male
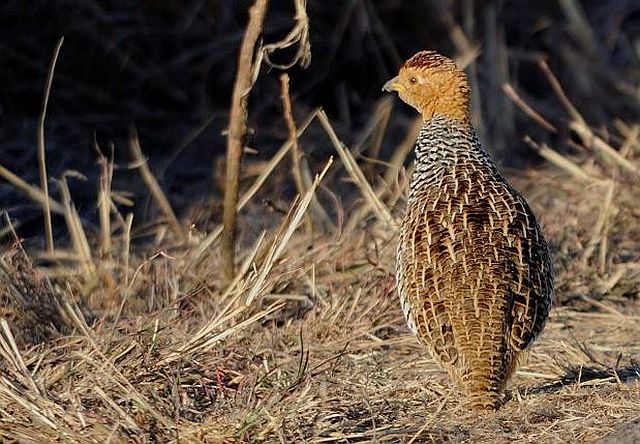
 © Flutterby
© Flutterby
Pilanesberg, Male
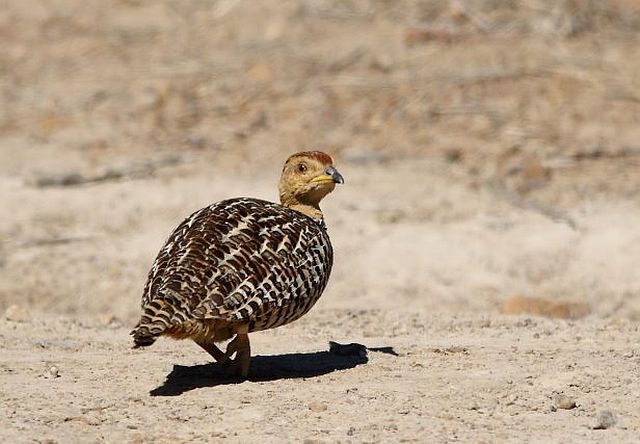
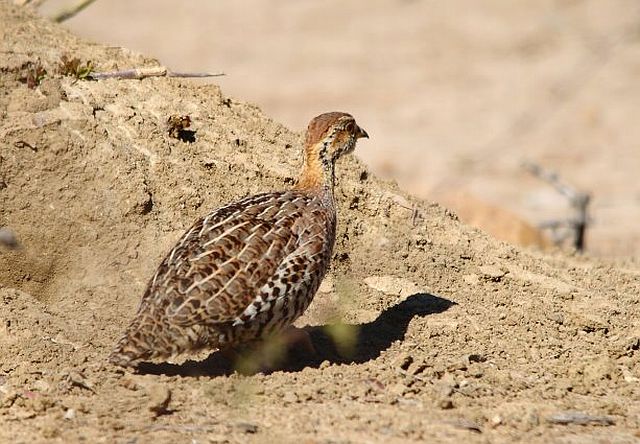 © Flutterby
© Flutterby
Pilanesberg, Female
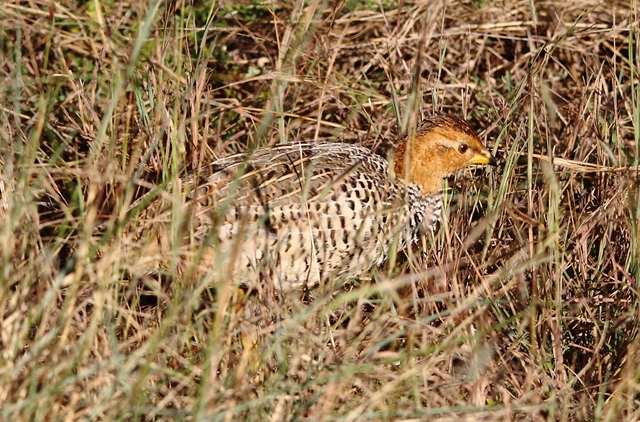 © Flutterby
© Flutterby
Kruger National Park, H1-1
Links:
Sabap2
Species text in The Atlas of Southern African Birds
 © lowveldboy
© lowveldboyMale
 © Dewi
© DewiMale
 © Flutterby
© FlutterbyPilanesberg, Male
 © Flutterby
© FlutterbyPilanesberg, Female
 © Flutterby
© FlutterbyKruger National Park, H1-1
Links:
Sabap2
Species text in The Atlas of Southern African Birds
-
Michele Nel
- Posts: 1994
- Joined: Mon Sep 10, 2012 10:19 am
- Country: South Africa
- Location: Cape Town
- Contact:
Grey-winged Francolin
190. Grey-winged Francolin Scleroptila afra (Bergpatrys)
Order: Galliformes. Family: Phasianidae
Description
A mainly grey francolin, the throat well spotted with black, the underparts closely barred black.
The plumage of male and female is the same but the male can be distinguished by its long, sharp leg spurs.
Immature has more white about the throat and the barring of the underparts extneds to the lower neck.
Similar species: Similar to other Francolins; range overlaps with Red-winged Francolin, Orange River Francolin, and (marginally) Shelley's Francolin. In flight, there is proportionally more grey than red on the wings compared to the other species, the red on the wings is confined to the outer wings. The throat is grey and freckled (white or buff in other species). Also differs from Shelley's Francolin in having narrow rather than bold barring on the belly.
Distribution
Endemic to South Africa and Lesotho (also a single record from eSwatini).
Habitat
Found in montane grasslands in the Drakensberg region (mainly above 1800 m elevation) and also occurs in karoo scrub, renosterbos and strandveld in the Western and Eastern Cape provinces. Adults tend to be very sedentary in habit, but young birds move around locally.
Diet
Mainly bulbs and corms or small sedges during non-breeding season, supplemented by insects during breeding period.
Breeding
Monogamous and territorial. The nest is a scrape in the ground, lined with grass and well concealed under a grass tuft. Four to eight eggs are laid July-December (winter rainfall areas in Western Cape) or August-March (summer rainfall areas). After all the eggs have been laid, they are incubated by the female for 21-23 days. Chicks leave the nest soon after hatching and accompany their parents through the breeding season. They can take short flights after 14-21 days.
Call
High-pitched ringing pip-pip-pip pi-pip wi-pleeu and variations thereof.
Listen to Bird Call.
Status: Fairly common resident. Endemic.
Order: Galliformes. Family: Phasianidae
Description
A mainly grey francolin, the throat well spotted with black, the underparts closely barred black.
The plumage of male and female is the same but the male can be distinguished by its long, sharp leg spurs.
Immature has more white about the throat and the barring of the underparts extneds to the lower neck.
Similar species: Similar to other Francolins; range overlaps with Red-winged Francolin, Orange River Francolin, and (marginally) Shelley's Francolin. In flight, there is proportionally more grey than red on the wings compared to the other species, the red on the wings is confined to the outer wings. The throat is grey and freckled (white or buff in other species). Also differs from Shelley's Francolin in having narrow rather than bold barring on the belly.
Distribution
Endemic to South Africa and Lesotho (also a single record from eSwatini).
Habitat
Found in montane grasslands in the Drakensberg region (mainly above 1800 m elevation) and also occurs in karoo scrub, renosterbos and strandveld in the Western and Eastern Cape provinces. Adults tend to be very sedentary in habit, but young birds move around locally.
Diet
Mainly bulbs and corms or small sedges during non-breeding season, supplemented by insects during breeding period.
Breeding
Monogamous and territorial. The nest is a scrape in the ground, lined with grass and well concealed under a grass tuft. Four to eight eggs are laid July-December (winter rainfall areas in Western Cape) or August-March (summer rainfall areas). After all the eggs have been laid, they are incubated by the female for 21-23 days. Chicks leave the nest soon after hatching and accompany their parents through the breeding season. They can take short flights after 14-21 days.
Call
High-pitched ringing pip-pip-pip pi-pip wi-pleeu and variations thereof.
Listen to Bird Call.
Status: Fairly common resident. Endemic.
-
Michele Nel
- Posts: 1994
- Joined: Mon Sep 10, 2012 10:19 am
- Country: South Africa
- Location: Cape Town
- Contact:
Grey-winged Francolin Photos
190. Grey-winged Francolin Scleroptila afra
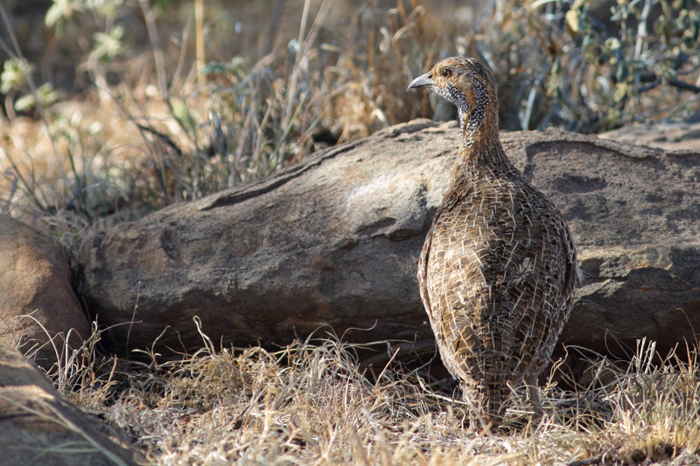
 © Puff Addy
© Puff Addy
Mountain Zebra National Park
Links:
Sabap2
Bioversity Explorer

 © Puff Addy
© Puff AddyMountain Zebra National Park
Links:
Sabap2
Bioversity Explorer
- Flutterby
- Posts: 44029
- Joined: Sat May 19, 2012 12:28 pm
- Country: South Africa
- Location: Gauteng, South Africa
- Contact:
Shelley's Francolin
191. Shelley's Francolin Scleroptila shelleyi (Laeveldpatrys)
Order: Galliformes Family: Phasianidae
Description
Length 28-31 cm. Clear white stripe through the eye and ear coverts. Boldly marked black border to white throat, the breast and flanks have chestnut stripes, and the belly is barred black and white. Male and female have the same plumage. Legs dull yellow.
Male can be distinguised by having tarsal spurs.
Juveniles resemble adults.
Similar species: The 'grassland francolins' (genus Scleroptila), which include the Orange River, Grey-winged, Red-winged and Shelley's francolins, are quite similar to one another. Shelley's Francolin can be distinguished by the black-and-white patterning on the lower breast and belly, which contrasts with the chestnut and buff patterned upper breast. It differs from the Grey-winged Francolin in having a white, not grey-freckled throat.
Distribution
Shelley’s Francolin has a patchy distribution in eastern Africa, southwards from Kenya. In southern Africa it occurs in Zimbabwe, north eastern parts of South Africa and Swaziland. In Zimbabwe it occurs on the central plateau, the eastern highlands and the Zambezi Valley, occurring as far west as the Botswana border, and it avoids the Limpopo Valley. In South Africa it also largely avoids the dry Limpopo Valley and is found in the central Transvaal and lowveld woodlands. It is widespread in Swaziland, and in KwaZulu-Natal north of about 30°S.
Habitat
Favours tall moist sweetveld grassland and open wooded savanna, often on stony terrain or among rocky outcrops.
Diet
Corms, bulbs and seeds in winter with increased insect intake during the breeding season.
Breeding
Momogamous. Usually lays 4-5 eggs in a shallow scrape well-concealed in grassland or under bush. Breeding season (laying dates): Zimbabwe: August to June (peak September - October; March to April); South Africa: peak October to January. After the 3-8 eggs have been laid, they are incubated by the female for 20-22 days. Chicks leave the nest soon after hatching and after 12 days are able to fly short distances, and after 5 weeks they can fly strongly.
Call
Very distinctive 4-note call I'll drink YOUR beer, repeated 3-4 times.
Status
Generally uncommon resident, sedentary and forming coveys of 4-8 birds during non-breeding season.
Order: Galliformes Family: Phasianidae
Description
Length 28-31 cm. Clear white stripe through the eye and ear coverts. Boldly marked black border to white throat, the breast and flanks have chestnut stripes, and the belly is barred black and white. Male and female have the same plumage. Legs dull yellow.
Male can be distinguised by having tarsal spurs.
Juveniles resemble adults.
Similar species: The 'grassland francolins' (genus Scleroptila), which include the Orange River, Grey-winged, Red-winged and Shelley's francolins, are quite similar to one another. Shelley's Francolin can be distinguished by the black-and-white patterning on the lower breast and belly, which contrasts with the chestnut and buff patterned upper breast. It differs from the Grey-winged Francolin in having a white, not grey-freckled throat.
Distribution
Shelley’s Francolin has a patchy distribution in eastern Africa, southwards from Kenya. In southern Africa it occurs in Zimbabwe, north eastern parts of South Africa and Swaziland. In Zimbabwe it occurs on the central plateau, the eastern highlands and the Zambezi Valley, occurring as far west as the Botswana border, and it avoids the Limpopo Valley. In South Africa it also largely avoids the dry Limpopo Valley and is found in the central Transvaal and lowveld woodlands. It is widespread in Swaziland, and in KwaZulu-Natal north of about 30°S.
Habitat
Favours tall moist sweetveld grassland and open wooded savanna, often on stony terrain or among rocky outcrops.
Diet
Corms, bulbs and seeds in winter with increased insect intake during the breeding season.
Breeding
Momogamous. Usually lays 4-5 eggs in a shallow scrape well-concealed in grassland or under bush. Breeding season (laying dates): Zimbabwe: August to June (peak September - October; March to April); South Africa: peak October to January. After the 3-8 eggs have been laid, they are incubated by the female for 20-22 days. Chicks leave the nest soon after hatching and after 12 days are able to fly short distances, and after 5 weeks they can fly strongly.
Call
Very distinctive 4-note call I'll drink YOUR beer, repeated 3-4 times.
Status
Generally uncommon resident, sedentary and forming coveys of 4-8 birds during non-breeding season.
Orange River Francolin
193. Orange River Francolin Scleroptila gutturalis (Kalaharipatrys)
Order: Galliformes Family: Phasianidae
Description
34 cm. A medium sized francolin with cryptic grey-brown upperparts, rufous barring with buff shaft streaks. Note the white throat is unmarked all white, bordered by narrow black band.
Upperparts overall grey-brown, feathers with white shafts, and pale buff central stripes and transverse bars. A narrow black-and-white band runs down sides of neck from behind eye; does not form necklace. Black moustachial stripe extends as a second black-and-white band that does join as a necklace around white throat. Upper breast and flank feathers buff, with large red-brown blotches; belly feathers buff, with indistinct black-and-white barring (racially variable). In flight, outer secondaries, primaries, and primary coverts extensively rufous. Bill decurved and grey, with yellow base to lower mandible. Eyes brown. Legs and feet yellow, male with tarsal spurs.
Juvenile: Lacks black collar; barred below.
Similar species: The 'grassland francolins' (genus Scleroptila), which include the Orange River, Grey-winged, Red-winged and Shelley's francolins, are quite similar to one another. The Orange River francolin is highly variable in plumage pattern and is most easily confused with the Red-winged Francolin from which it can be distinguished by having a thin, not broad, breast band. It differs from Shelley's Francolin in lacking bold black and white markings on the lower breast and belly and by only one of the facial stripes (the moustachial stripe) meeting on the breast to form the breast band. In Shelley's Francolin, both dark facial stripes meet on foreneck. It differs from Grey-winged Francolin in having a white, not grey-freckled, throat.
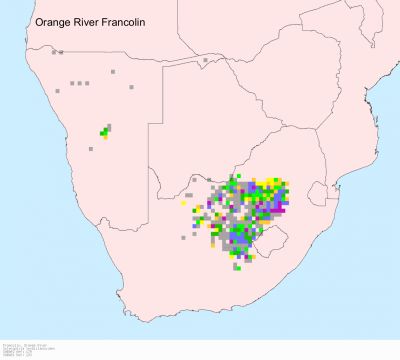
Distribution
Central South Africa, Botswana & Northern Namibia. From middle Orange River (around Aliwal North) and NE Karoo (around De Aar) to Angola; in South Africa mainly from dry W highveld, across Kalahari to Windhoek and Ovamboland.
S. g. archeri: s Ethiopia, se Sudan, n Uganda and nw Kenya
S. g. lorti: n Somalia
S. g. jugularis: sw Angola
S. g. pallidior: n Namibia
S. g. levalliantoides: e Namibia and s Botswana to c South Africa
Habitat
Open grasslands and savanna.
Diet
Corms, bulbs (e.g. Moraea species), seeds, berries, flowers, fallen grain, green shoots; insects in summer.
Breeding
Nest, which is built by the female, is a scrape in the ground, lined with dry grass and hidden in dense grass. Breeding season (laying dates): year round, depending on rainfall. After laying 3-8 eggs, the female incubates them for 20-23 days. Eggs are pale yellowish brown, speckled with darker brown. Young leave nest soon after hatching; start taking short flights after 12-14 days, and fly strongly after 5-6 weeks.
Call
A high pitched ki-keet ki-kit, often at dawn.
Status
A near endemic which is locally common in suitable habitat.
Order: Galliformes Family: Phasianidae
Description
34 cm. A medium sized francolin with cryptic grey-brown upperparts, rufous barring with buff shaft streaks. Note the white throat is unmarked all white, bordered by narrow black band.
Upperparts overall grey-brown, feathers with white shafts, and pale buff central stripes and transverse bars. A narrow black-and-white band runs down sides of neck from behind eye; does not form necklace. Black moustachial stripe extends as a second black-and-white band that does join as a necklace around white throat. Upper breast and flank feathers buff, with large red-brown blotches; belly feathers buff, with indistinct black-and-white barring (racially variable). In flight, outer secondaries, primaries, and primary coverts extensively rufous. Bill decurved and grey, with yellow base to lower mandible. Eyes brown. Legs and feet yellow, male with tarsal spurs.
Juvenile: Lacks black collar; barred below.
Similar species: The 'grassland francolins' (genus Scleroptila), which include the Orange River, Grey-winged, Red-winged and Shelley's francolins, are quite similar to one another. The Orange River francolin is highly variable in plumage pattern and is most easily confused with the Red-winged Francolin from which it can be distinguished by having a thin, not broad, breast band. It differs from Shelley's Francolin in lacking bold black and white markings on the lower breast and belly and by only one of the facial stripes (the moustachial stripe) meeting on the breast to form the breast band. In Shelley's Francolin, both dark facial stripes meet on foreneck. It differs from Grey-winged Francolin in having a white, not grey-freckled, throat.
Distribution
Central South Africa, Botswana & Northern Namibia. From middle Orange River (around Aliwal North) and NE Karoo (around De Aar) to Angola; in South Africa mainly from dry W highveld, across Kalahari to Windhoek and Ovamboland.
S. g. archeri: s Ethiopia, se Sudan, n Uganda and nw Kenya
S. g. lorti: n Somalia
S. g. jugularis: sw Angola
S. g. pallidior: n Namibia
S. g. levalliantoides: e Namibia and s Botswana to c South Africa

Habitat
Open grasslands and savanna.
Diet
Corms, bulbs (e.g. Moraea species), seeds, berries, flowers, fallen grain, green shoots; insects in summer.
Breeding
Nest, which is built by the female, is a scrape in the ground, lined with dry grass and hidden in dense grass. Breeding season (laying dates): year round, depending on rainfall. After laying 3-8 eggs, the female incubates them for 20-23 days. Eggs are pale yellowish brown, speckled with darker brown. Young leave nest soon after hatching; start taking short flights after 12-14 days, and fly strongly after 5-6 weeks.
Call
A high pitched ki-keet ki-kit, often at dawn.
Status
A near endemic which is locally common in suitable habitat.
Orange River Francolin Photos
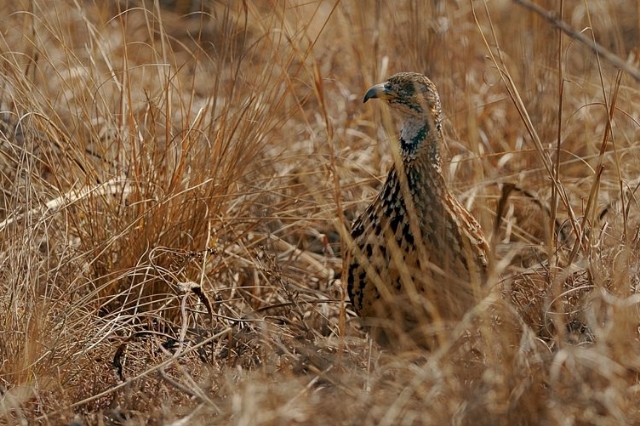
193. Orange River Francolin Scleroptila gutturalis
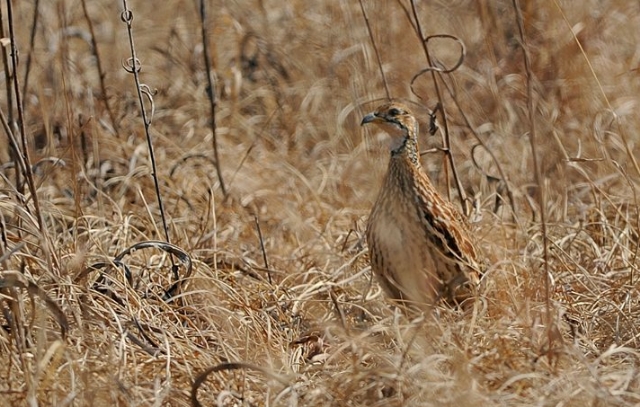 © Dewi
© Dewi
Rietvlei Nature Reserve, Gauteng
 © Dewi
© Dewi
Rietvlei Nature Reserve, Gauteng
 © BluTuna
© BluTuna
Marakele National Park
 © BluTuna
© BluTuna
Marakele National Park
Links:
Species text Sabap1
Sabap2
 © Dewi
© DewiRietvlei Nature Reserve, Gauteng
 © Dewi
© DewiRietvlei Nature Reserve, Gauteng
 © BluTuna
© BluTunaMarakele National Park
 © BluTuna
© BluTunaMarakele National Park
Links:
Species text Sabap1
Sabap2
Crested Francolin
189. Crested Francolin Dendroperdix sephaena (Bospatrys)
Order: Galliformes. Family: Phasianidae
Description
32 cm. Crested Francolins are flecked white and brown and have a broad white superciliary stripe, the cap is dark, the throat white. Deep red legs. Black bill. When alarmed, their dark crest feathers will stand up, like a mohawk. Its habit of cocking its tail is also a useful distinguishing feature.
Males can be distinguished from females and juveniles by their brighter plumage colours and upcurved spurs on their legs. Cap dark brown, grey outer edge contrasting with broad white supercilium. Narrow blackish eye stripe, bordered below with short white stripe extending back to rear of eye. Ear coverts uniformly sandy buff. Moustachial stripe speckled, chestnut. Hind neck flecked reddish brown, white and black. Remainder of upper parts cinnamon brown, some coverts with darker inner webs and all with white shafts and shaft streaks, creating distinctive striped appearance. Rump yellowish brown; tail feathers dark, almost black, diagnostic when fanned in flight. Chin and throat white, with very narrow, dark malar stripe. Foreneck and upper breast sandy buff, with triangular dark brown, white-edged markings, contrasting with paler throat and belly. Remainder of underparts sandy buff, with narrow, irregular, dark brown vermiculations, fading on vent to uniform pinkish. Bill dark grey. Eyes dark brown. Legs and feet purplish red, with long, upward curving tarsal spurs.
Female and juvenile are less boldly marked than the male and lack the long, upcurved leg spur of the male.
Juveniles are paler above.
Can be distinguished from other francolins by the broad white eye-stripe contrasting with the dark head, combined with the white throat.
Distribution
From Ethiopia down to the northern regions of southern Africa.
D. s. grantii: s Sudan and w Ethiopia to nc Tanzania
D. s. rovuma: e Kenya to n Mozambique
D. s. spilogaster: e Ethiopia, Somalia and ne Kenya
D. s. zambesiae : wc Mozambique to Namibia and s Angola
D. s. sephaena: e Zimbabwe to se Botswana, s Mozambique and ne South Africa
Habitat
Found in woodland and wooded savanna.
Diet
In summer it feeds mainly on insects while in winter it is mainly herbivorous (underground corms and bulbs, above ground shoots, leaves, fruits and berries).
Breeding
Form breeding pairs (monogamous) that can last for up to 10 months. Males compete and fight over females. Copulation follows a ritual display. Nest is hidden among grass and/or shrubs and consists of a scrape in the ground lined with grass and leaves. Breeding season coincides with rain: March to May peak in northern Namibia, Botswana and Zimbabwe; October to March in South Africa. 3-7 eggs are laid and after the clutch has been completed, it is incubated for 19-26 days, exclusively by the female. Meanwhile the male guards the general area around the nest and uses a warning call to alert the female to any approaching danger. Chicks leave the nest about 2 hours after hatching and are looked after by their parents.
Behaviour
The Crested Francolin is the only member of the Genus Dendroperdix, meaning 'a tree partridge'. This is a reference to their habit of communally (in groups called coveys) roosting huddled together in the canopy of a tree at night.
Call
Their repeated call is a loud, crowing chak, kikwerri-kwetchi, mostly at dusk and a chee-chakla, chee-chakla, in rattling duet. Listen to Bird Call.
Status
Common resident, found in conveys of 2-5 birds in non-breading season.
Order: Galliformes. Family: Phasianidae
Description
32 cm. Crested Francolins are flecked white and brown and have a broad white superciliary stripe, the cap is dark, the throat white. Deep red legs. Black bill. When alarmed, their dark crest feathers will stand up, like a mohawk. Its habit of cocking its tail is also a useful distinguishing feature.
Males can be distinguished from females and juveniles by their brighter plumage colours and upcurved spurs on their legs. Cap dark brown, grey outer edge contrasting with broad white supercilium. Narrow blackish eye stripe, bordered below with short white stripe extending back to rear of eye. Ear coverts uniformly sandy buff. Moustachial stripe speckled, chestnut. Hind neck flecked reddish brown, white and black. Remainder of upper parts cinnamon brown, some coverts with darker inner webs and all with white shafts and shaft streaks, creating distinctive striped appearance. Rump yellowish brown; tail feathers dark, almost black, diagnostic when fanned in flight. Chin and throat white, with very narrow, dark malar stripe. Foreneck and upper breast sandy buff, with triangular dark brown, white-edged markings, contrasting with paler throat and belly. Remainder of underparts sandy buff, with narrow, irregular, dark brown vermiculations, fading on vent to uniform pinkish. Bill dark grey. Eyes dark brown. Legs and feet purplish red, with long, upward curving tarsal spurs.
Female and juvenile are less boldly marked than the male and lack the long, upcurved leg spur of the male.
Juveniles are paler above.
Can be distinguished from other francolins by the broad white eye-stripe contrasting with the dark head, combined with the white throat.
Distribution
From Ethiopia down to the northern regions of southern Africa.
D. s. grantii: s Sudan and w Ethiopia to nc Tanzania
D. s. rovuma: e Kenya to n Mozambique
D. s. spilogaster: e Ethiopia, Somalia and ne Kenya
D. s. zambesiae : wc Mozambique to Namibia and s Angola
D. s. sephaena: e Zimbabwe to se Botswana, s Mozambique and ne South Africa
Habitat
Found in woodland and wooded savanna.
Diet
In summer it feeds mainly on insects while in winter it is mainly herbivorous (underground corms and bulbs, above ground shoots, leaves, fruits and berries).
Breeding
Form breeding pairs (monogamous) that can last for up to 10 months. Males compete and fight over females. Copulation follows a ritual display. Nest is hidden among grass and/or shrubs and consists of a scrape in the ground lined with grass and leaves. Breeding season coincides with rain: March to May peak in northern Namibia, Botswana and Zimbabwe; October to March in South Africa. 3-7 eggs are laid and after the clutch has been completed, it is incubated for 19-26 days, exclusively by the female. Meanwhile the male guards the general area around the nest and uses a warning call to alert the female to any approaching danger. Chicks leave the nest about 2 hours after hatching and are looked after by their parents.
Behaviour
The Crested Francolin is the only member of the Genus Dendroperdix, meaning 'a tree partridge'. This is a reference to their habit of communally (in groups called coveys) roosting huddled together in the canopy of a tree at night.
Call
Their repeated call is a loud, crowing chak, kikwerri-kwetchi, mostly at dusk and a chee-chakla, chee-chakla, in rattling duet. Listen to Bird Call.
Status
Common resident, found in conveys of 2-5 birds in non-breading season.
Crested Francolin Photos
189. Crested Francolin Dendroperdix sephaena
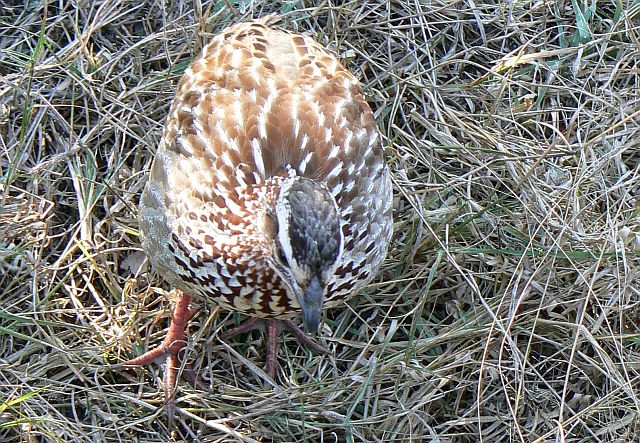 © Toko
© Toko
Kruger National Park
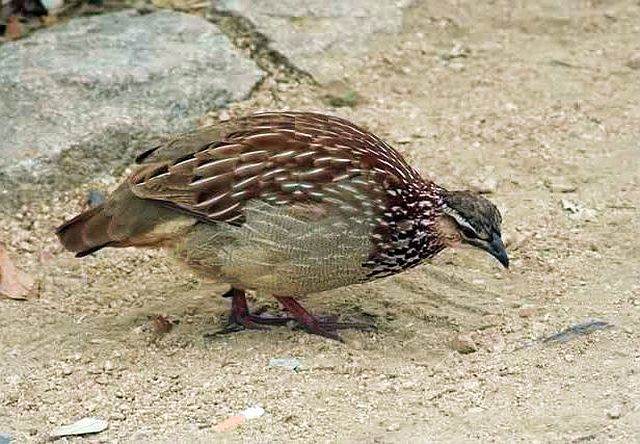 © pooky
© pooky
Male
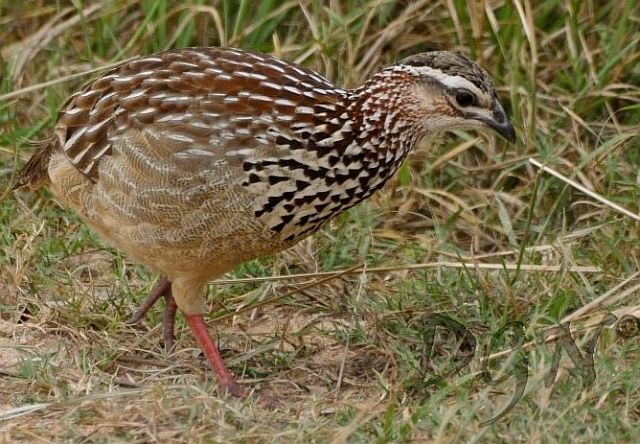 © JustN@ture
© JustN@ture
Female
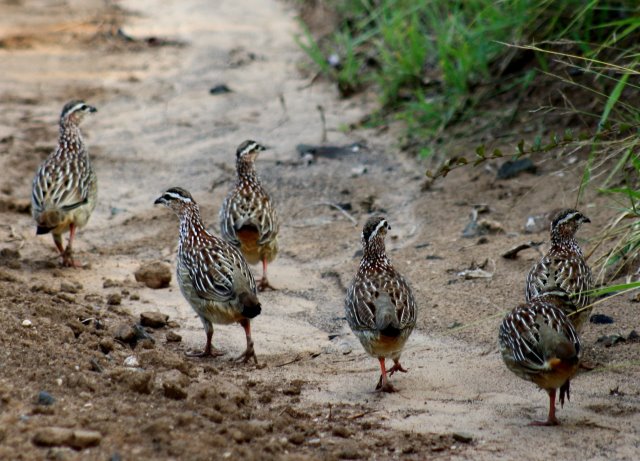 © Flutterby
© Flutterby
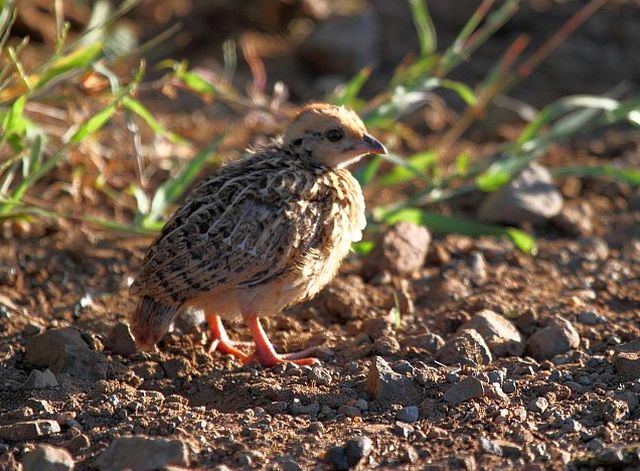 © Duke
© Duke
Chick, Kruger National Park, S35
Links:
Sabap2
Species text in The Atlas of Southern African Birds
Oiseaux net - Francolin huppé
 © Toko
© TokoKruger National Park
 © pooky
© pookyMale
 © JustN@ture
© JustN@tureFemale
 © Flutterby
© Flutterby © Duke
© DukeChick, Kruger National Park, S35
Links:
Sabap2
Species text in The Atlas of Southern African Birds
Oiseaux net - Francolin huppé



