Schalow's Turaco
Posted: Mon Mar 10, 2014 5:49 pm
370. Schalow's Turaco Tauraco schalowi
ORDER MUSOPHAGIFORMES. Family Musophagidae
Description
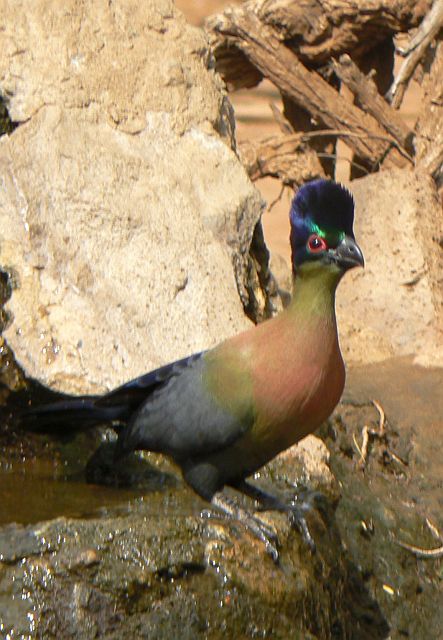
41–44 cm; male 236–261 g, female 208–267 g. Large, predominantly green turaco. Similar to T. livingstonii, best identified by very long, white-tipped, floppy forward-pointing crest. Also has a bright red bill, and a hhort white line above and a longer one below and behind the red-ringed eyes. Wings green washed blue, tail dark glossed prurple-black. Their wings are short and round with red flight feathers meant for short flights.
Distribution
Occurs from western Angola and southern DRC to Tanzania, Zambia, the Caprivi Strip (Namibia) and northern Botswana.
Movements and migrations
Resident and largely sedentary, although it may occasionally make nomadic movements.
Habitat
Lowland evergreen forest.
Diet
Mainly eats fruit, doing most of its foraging in the forest canopy and understorey.
Breeding
Monogamous, territorial solitary nester, its nest is yet to be described, although it is known that it can be placed quite high up in a tree. Egg-laying season is from September-February in Zambia and Malawi. It lays 1-2 eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for about 20-22 days. The chicks leave the nest at about 25-28 days old; within two weeks they have learnt to fly and are feeding for themselves, becoming fully independent at about 53 days old.
Status
Locally common resident.
ORDER MUSOPHAGIFORMES. Family Musophagidae
Description
41–44 cm; male 236–261 g, female 208–267 g. Large, predominantly green turaco. Similar to T. livingstonii, best identified by very long, white-tipped, floppy forward-pointing crest. Also has a bright red bill, and a hhort white line above and a longer one below and behind the red-ringed eyes. Wings green washed blue, tail dark glossed prurple-black. Their wings are short and round with red flight feathers meant for short flights.
Distribution
Occurs from western Angola and southern DRC to Tanzania, Zambia, the Caprivi Strip (Namibia) and northern Botswana.
Movements and migrations
Resident and largely sedentary, although it may occasionally make nomadic movements.
Habitat
Lowland evergreen forest.
Diet
Mainly eats fruit, doing most of its foraging in the forest canopy and understorey.
Breeding
Monogamous, territorial solitary nester, its nest is yet to be described, although it is known that it can be placed quite high up in a tree. Egg-laying season is from September-February in Zambia and Malawi. It lays 1-2 eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for about 20-22 days. The chicks leave the nest at about 25-28 days old; within two weeks they have learnt to fly and are feeding for themselves, becoming fully independent at about 53 days old.
Status
Locally common resident.
 © Dewi
© Dewi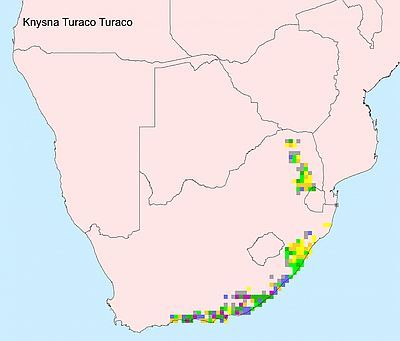
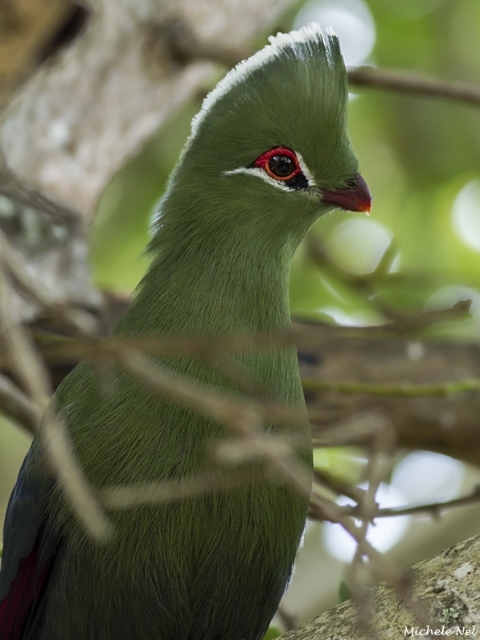 © Michele Nel
© Michele Nel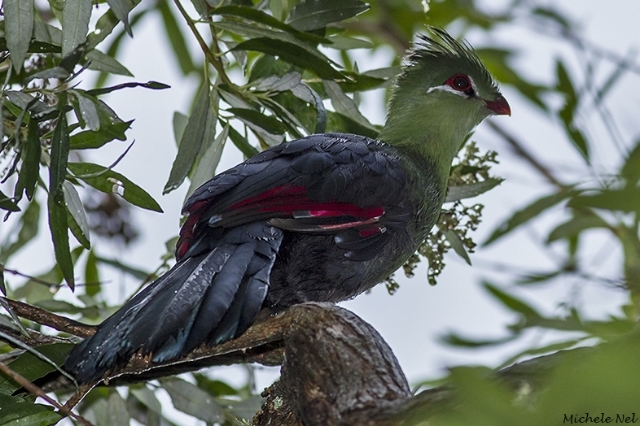 © Michele Nel
© Michele Nel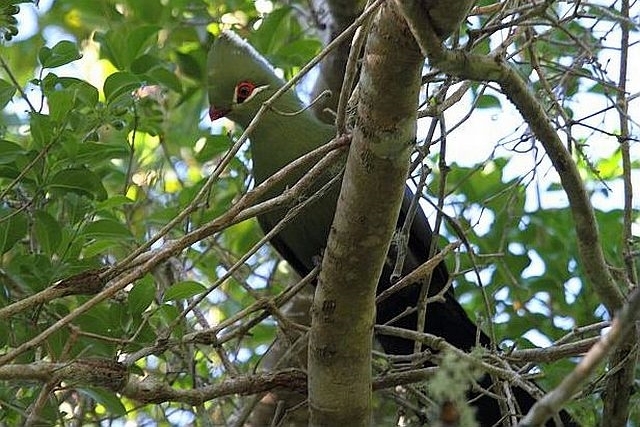 © Duke
© Duke
 © Toko
© Toko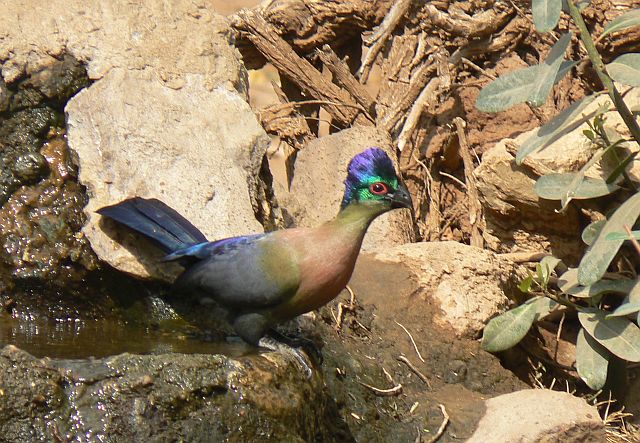 © Toko
© Toko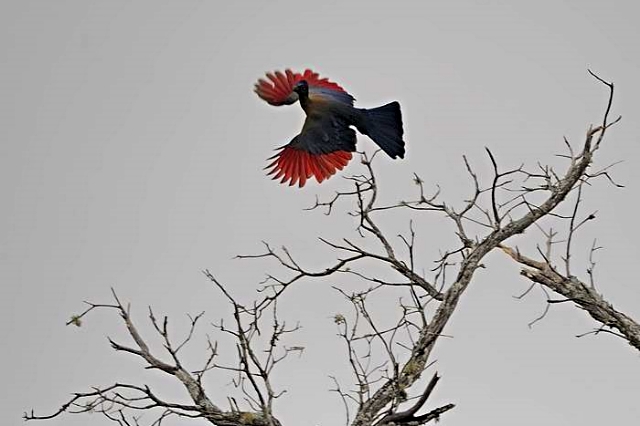 © Dewi
© Dewi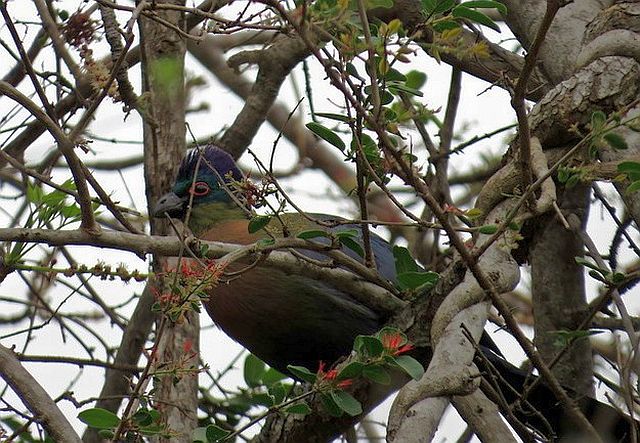 © The Cow
© The Cow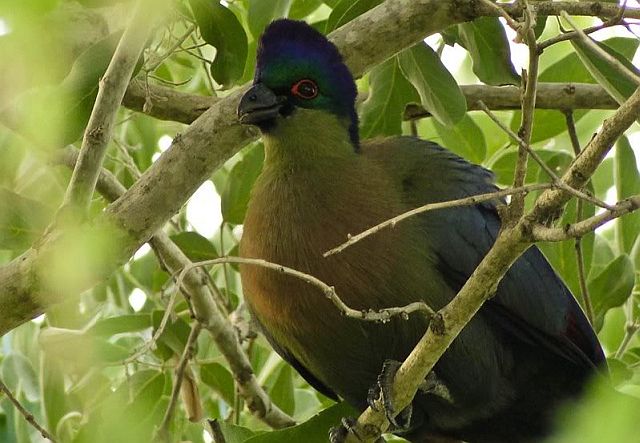 © JustN@ture
© JustN@ture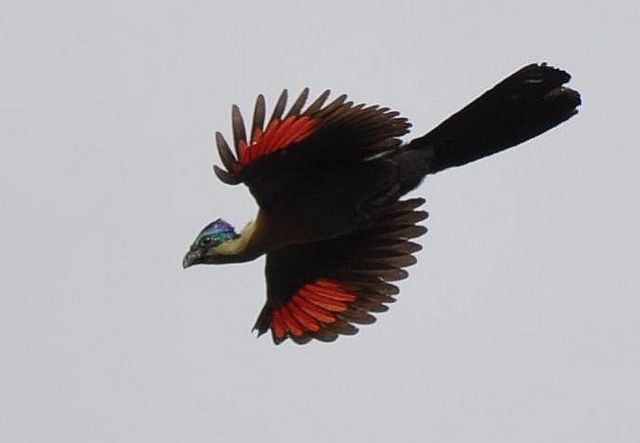 © steamtrainfan
© steamtrainfan © BluTuna
© BluTuna © Dewi
© Dewi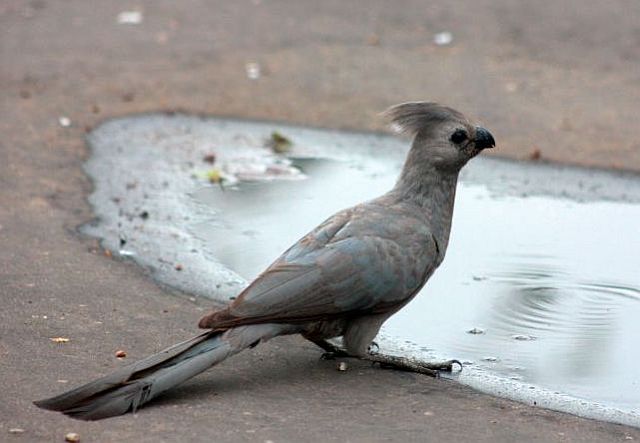 © harrys
© harrys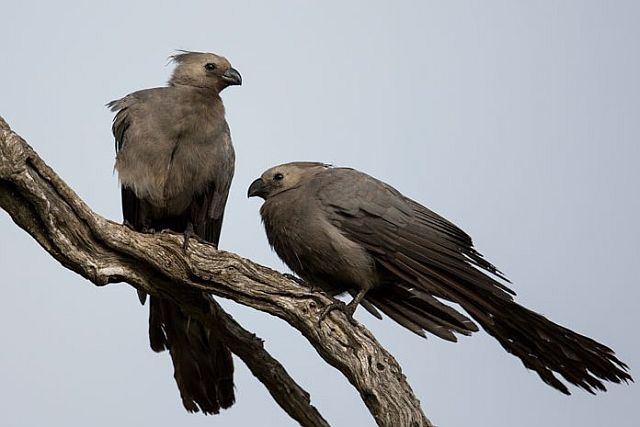 © Pumbaa
© Pumbaa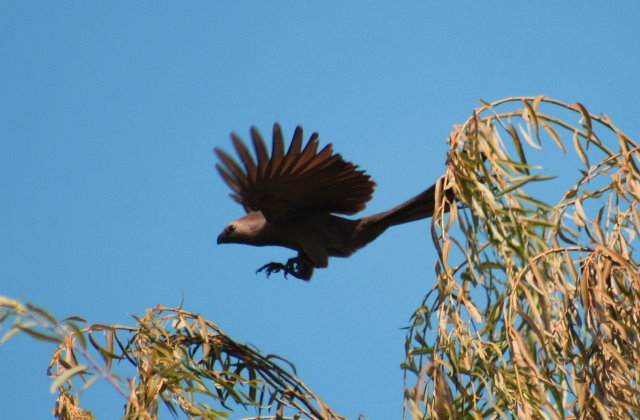  © Flutterby
© Flutterby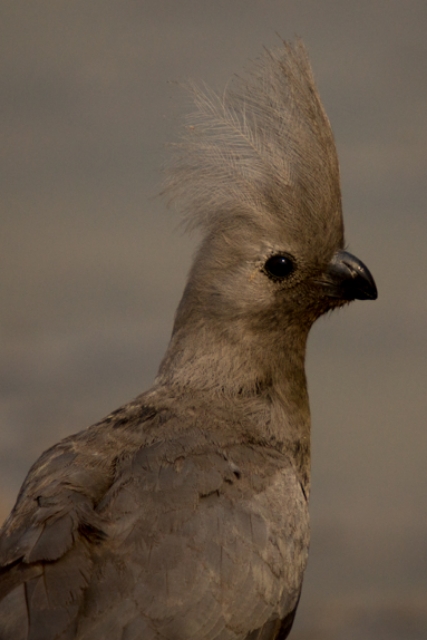 © Kesheshe
© Kesheshe