Southern Yellow-billed Hornbill
Posted: Thu Mar 13, 2014 2:49 pm
459. Southern Yellow-billed Hornbill Tockus leucomelas (Geelbekneushoringvoël)
Order: Bucerotiformes. Family: Bucerotidae
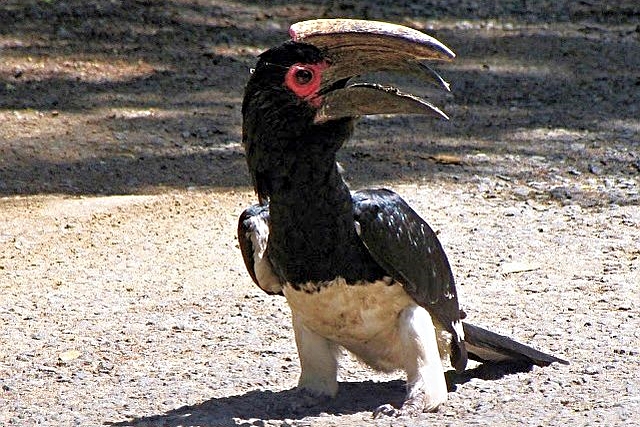
Description: 48-60 cm. White belly. Grey neck. Black back covered with white spots and stripe. Yellow bill. Bare red skin around eyes and malar stripe. Eyes yellow. Sexes alike.
Juvenile has smaller bill and is more dusky; eyes grey becoming brown.
Distribution
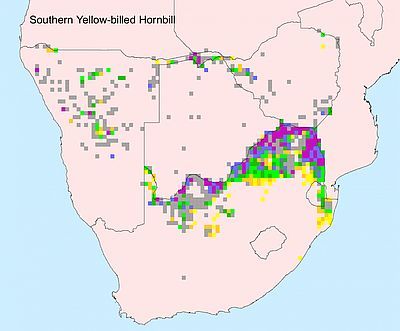
Inland southern Africa (western and southern Angola, southern Zambia, northern Namibia, Botswana, north-central and north-eastern South Africa, Zimbabwe, western and southern Mozambique, and Swaziland).
Habitat
Wide range of savanna and more closed woodland.
Diet:
They feed mainly on the ground foraging for seeds, small insects, spiders and scorpions. They also eat small vertebrates, eggs, fruit, seeds and young leaves. Termites and ants are a preferred food source in the dry season.
Breeding
Monogamous. It nests in natural tree holes up to about 12 m above ground, lining the chamber with dry leaves and small bark flakes. The entrance is sealed by the female from the inside with her own faeces, leaving a vertical slit 5-15 mm wide. Egg-laying season always follows good rains, usually peaking from September-October. The clutch consists of 3 to 4 white eggs. Incubation by the female lasts for or about 25 days, the male feeds the female through the narrow slit. The chicks stay in the nest for 42-47 days, remaining near the nest for a few more days before joining their parents in foraging trips. When the oldest chick is 19-27 days old the female leaves the nest for the first time since laying the eggs.
Call
Long series of clucking notes kok kok kok korkorkorkorkor. Listen to Bird Call.
Status
Common, widespread resident and near-endemic. Usually in pairs or small family groups in non-breeding season.
Order: Bucerotiformes. Family: Bucerotidae
Description: 48-60 cm. White belly. Grey neck. Black back covered with white spots and stripe. Yellow bill. Bare red skin around eyes and malar stripe. Eyes yellow. Sexes alike.
Juvenile has smaller bill and is more dusky; eyes grey becoming brown.
Distribution
Inland southern Africa (western and southern Angola, southern Zambia, northern Namibia, Botswana, north-central and north-eastern South Africa, Zimbabwe, western and southern Mozambique, and Swaziland).

Habitat
Wide range of savanna and more closed woodland.
Diet:
They feed mainly on the ground foraging for seeds, small insects, spiders and scorpions. They also eat small vertebrates, eggs, fruit, seeds and young leaves. Termites and ants are a preferred food source in the dry season.
Breeding
Monogamous. It nests in natural tree holes up to about 12 m above ground, lining the chamber with dry leaves and small bark flakes. The entrance is sealed by the female from the inside with her own faeces, leaving a vertical slit 5-15 mm wide. Egg-laying season always follows good rains, usually peaking from September-October. The clutch consists of 3 to 4 white eggs. Incubation by the female lasts for or about 25 days, the male feeds the female through the narrow slit. The chicks stay in the nest for 42-47 days, remaining near the nest for a few more days before joining their parents in foraging trips. When the oldest chick is 19-27 days old the female leaves the nest for the first time since laying the eggs.
Call
Long series of clucking notes kok kok kok korkorkorkorkor. Listen to Bird Call.
Status
Common, widespread resident and near-endemic. Usually in pairs or small family groups in non-breeding season.
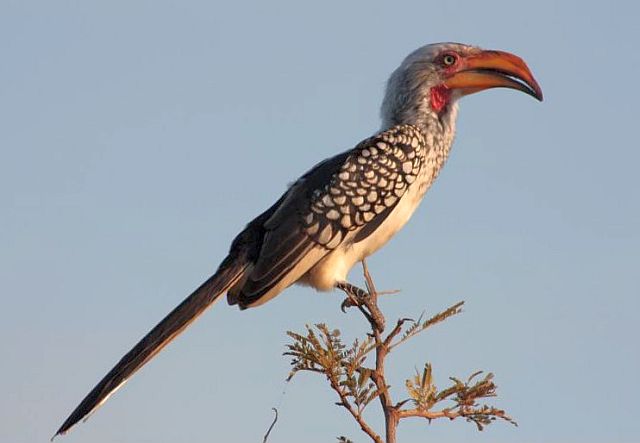 © harrys
© harrys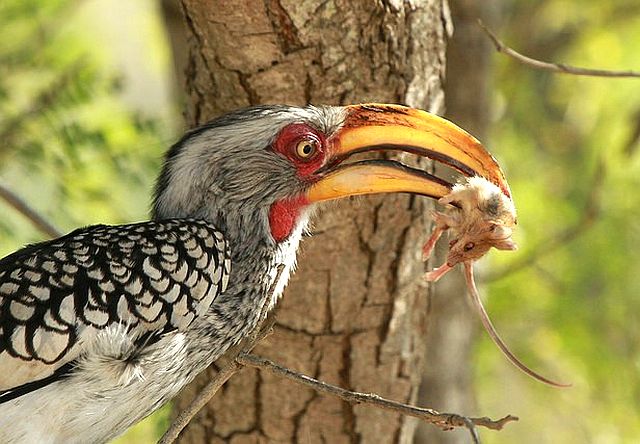 © flying cheetah
© flying cheetah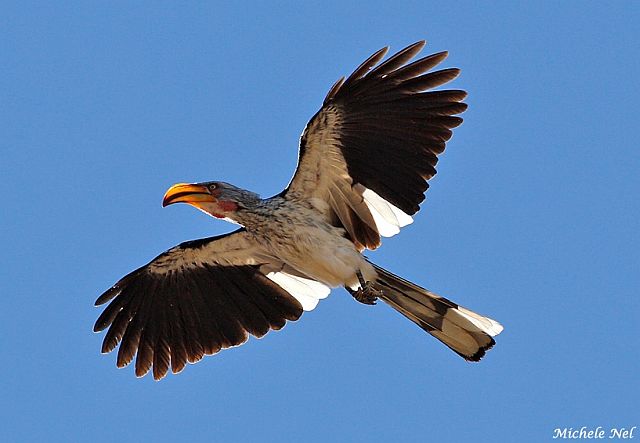 © Michele Nel
© Michele Nel
 © Lisbeth
© Lisbeth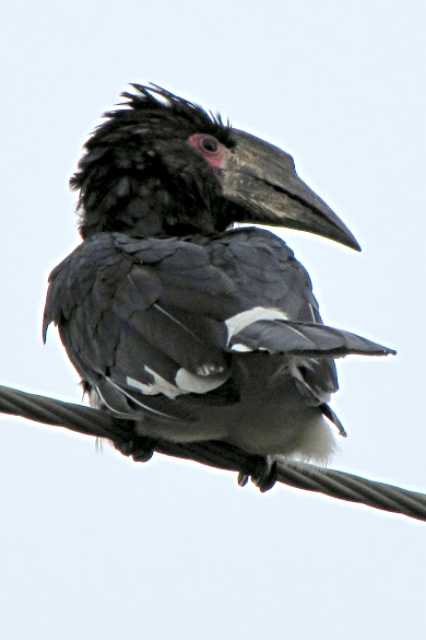 © Lisbeth
© Lisbeth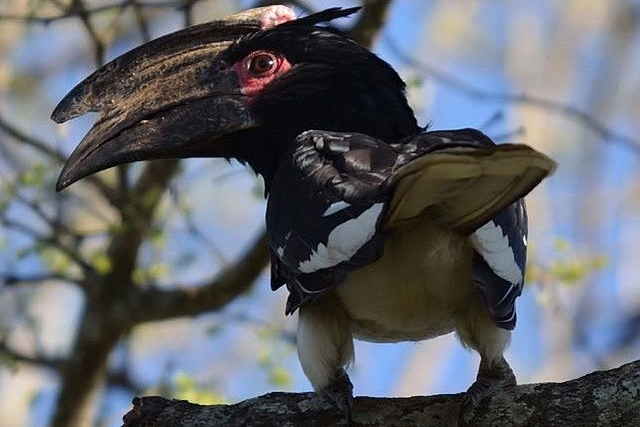 © BluTuna
© BluTuna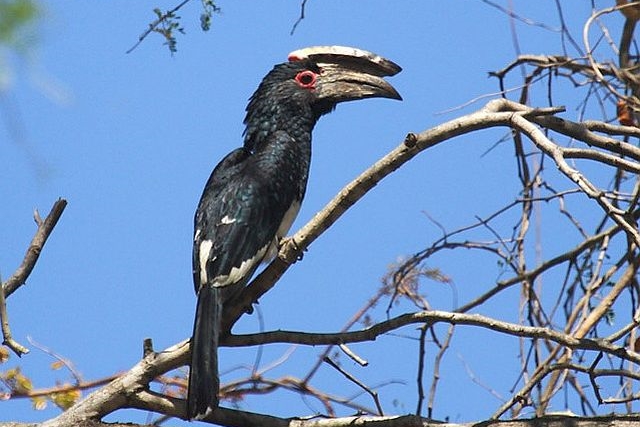 © leachy
© leachy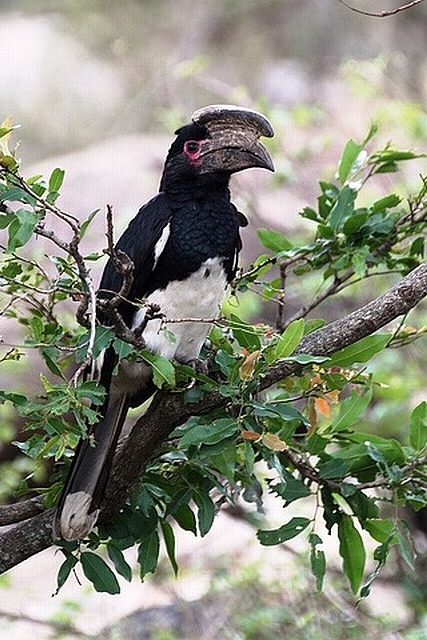 © Moggiedog
© Moggiedog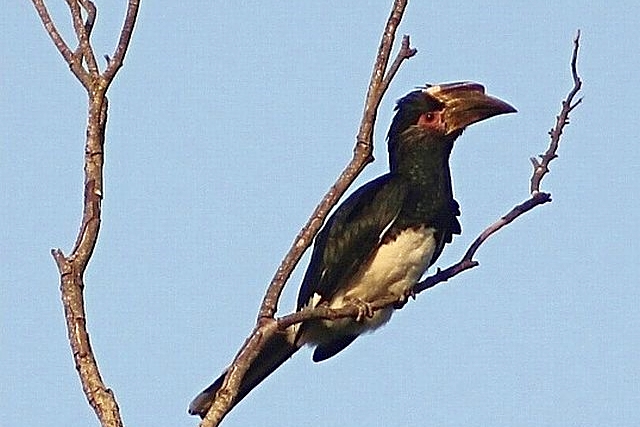 © Amoli
© Amoli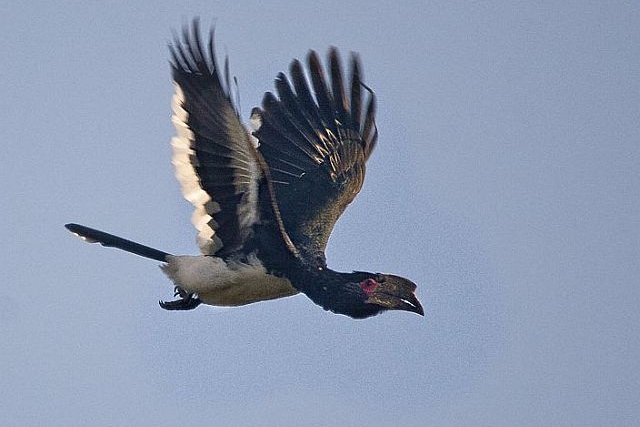 © PRWIN
© PRWIN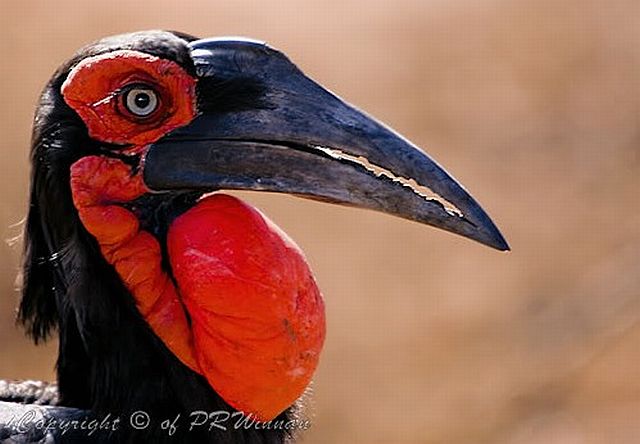
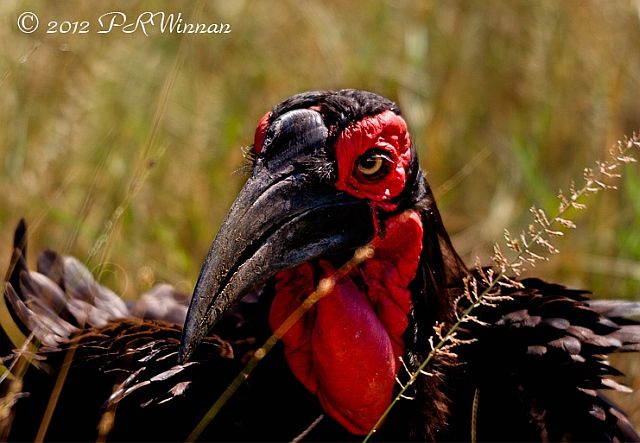
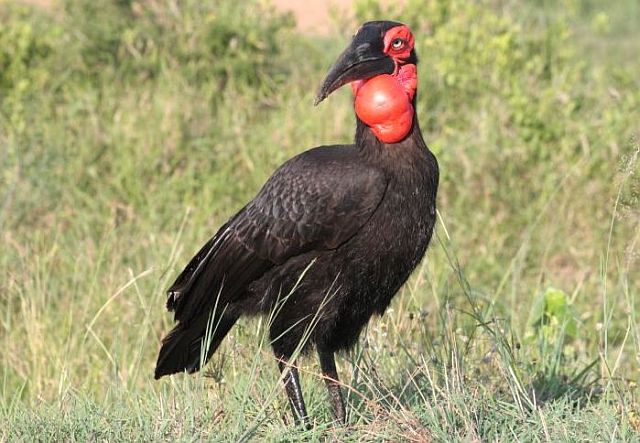
 © harrys
© harrys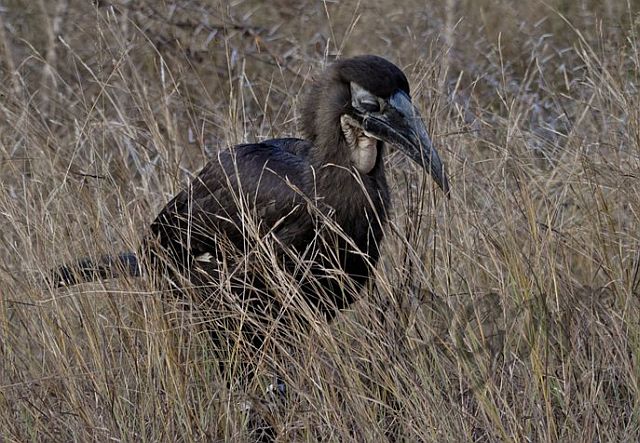 © JustN@ture
© JustN@ture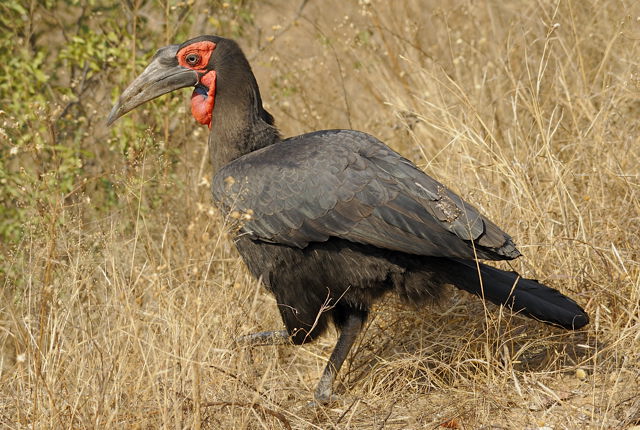 © Dewi
© Dewi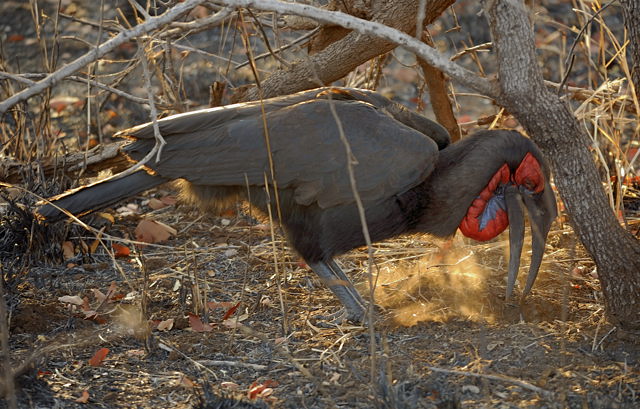 © Dewi
© Dewi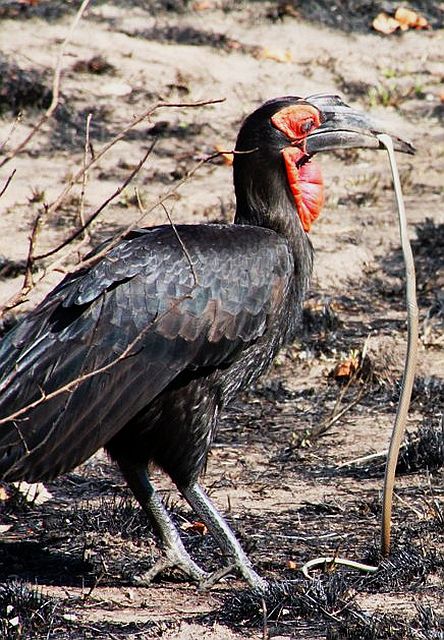 © dup
© dup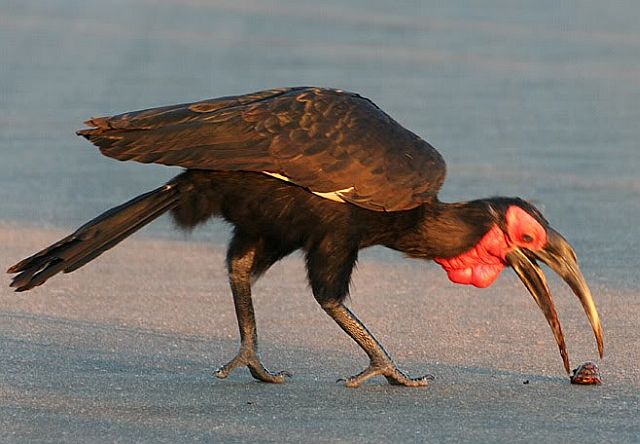 © leachy
© leachy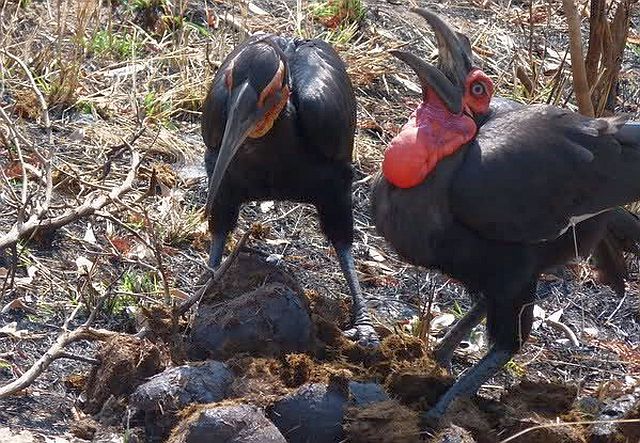 © Bushcraft
© Bushcraft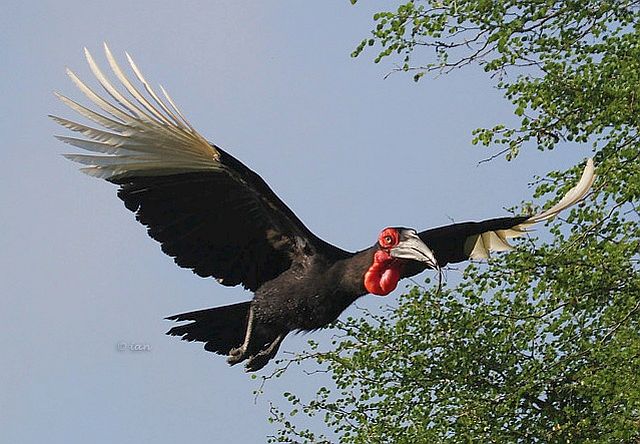 © leachy
© leachy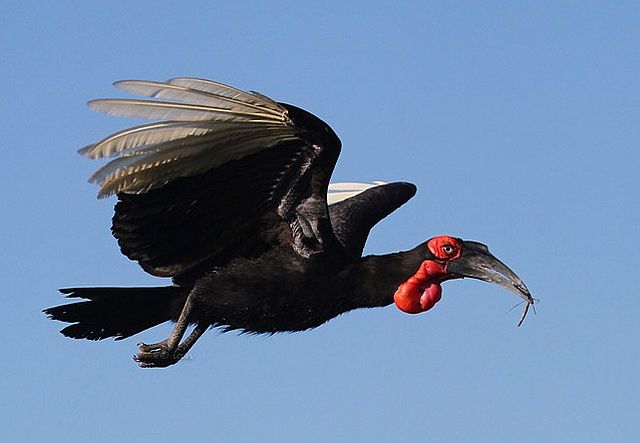 © leachy
© leachy