The real economic value of Greater Kruger National Park
Posted: Fri Jul 10, 2020 3:35 pm
Posted on July 8, 2020 by Team Africa Geographic in the DECODING SCIENCE post series.
A 2020 study has revealed the considerable economic contributions of the Kruger National Park and the surrounding “contiguous reserves” that together compose the Greater Kruger National Park (GKNP). The study is a joint effort between researchers from the University of Florida and South African National Parks (SANParks).
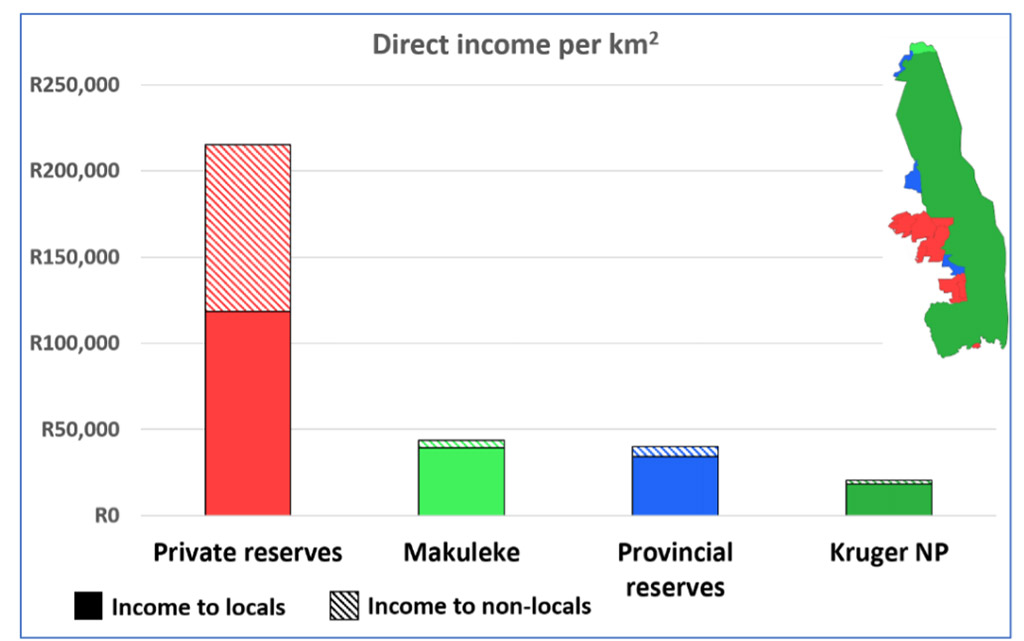
In considering the public, private, and community-owned components as a whole, the study attributes different values in financial, social, and political domains to each. The researchers suggest that the GKNP should be considered as a whole when working towards management frameworks and policies. The private reserves, while constituting only 12% of the total land area, were responsible for over 60% of the total employment, tax and GDP contributions. Conversely, the Kruger National Park accounts for almost all domestic visits, performing a vital political and social function.
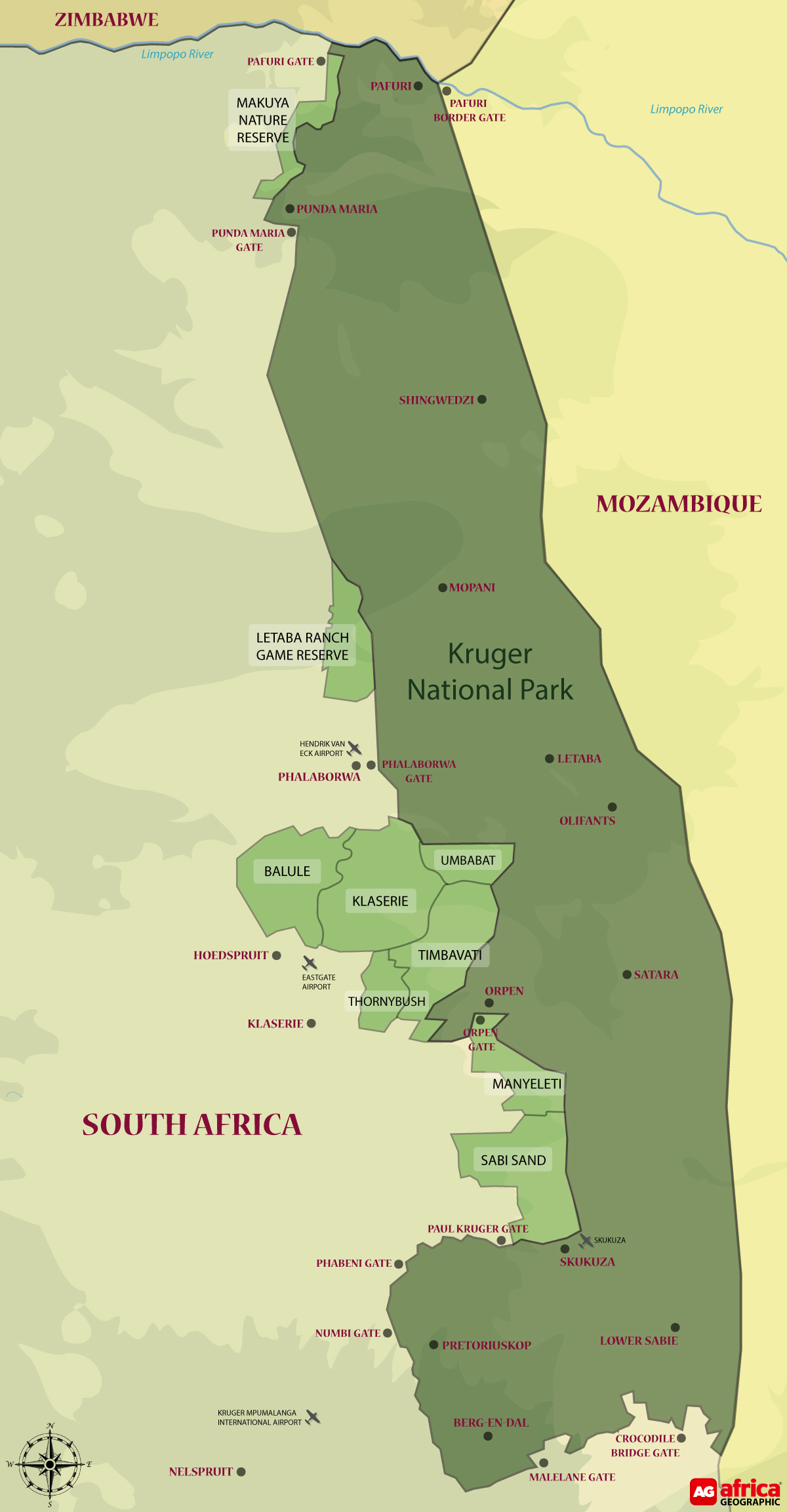
Across the total 22,686km² (23 million hectares) of the entire open system, there are close to 8,000 beds and some 700 different camp and lodge sites. As a general rule, the Kruger National Park itself is oriented towards budget self-catering options, while the private reserves tend to cater to more luxury, high-end safari experiences. For the study, anyone living within 50km of the GKNP boundary fence was considered to be “local”, which equated to approximately 2.9 million people, including many in semi-rural and socio-economically disadvantaged communities. The study reveals that from a period between 2016-2017, there were 3.5 million bed nights and day-visits to the GKNP, of which 35% on average were foreign tourists. As would be expected, the highest visitation by far was to the Kruger National Park itself, while the provincial reserves (Manyeleti Nature Reserve, Letaba Ranch Game Reserve and Makuya Nature Reserve) accounted for only 1% of the total visits.
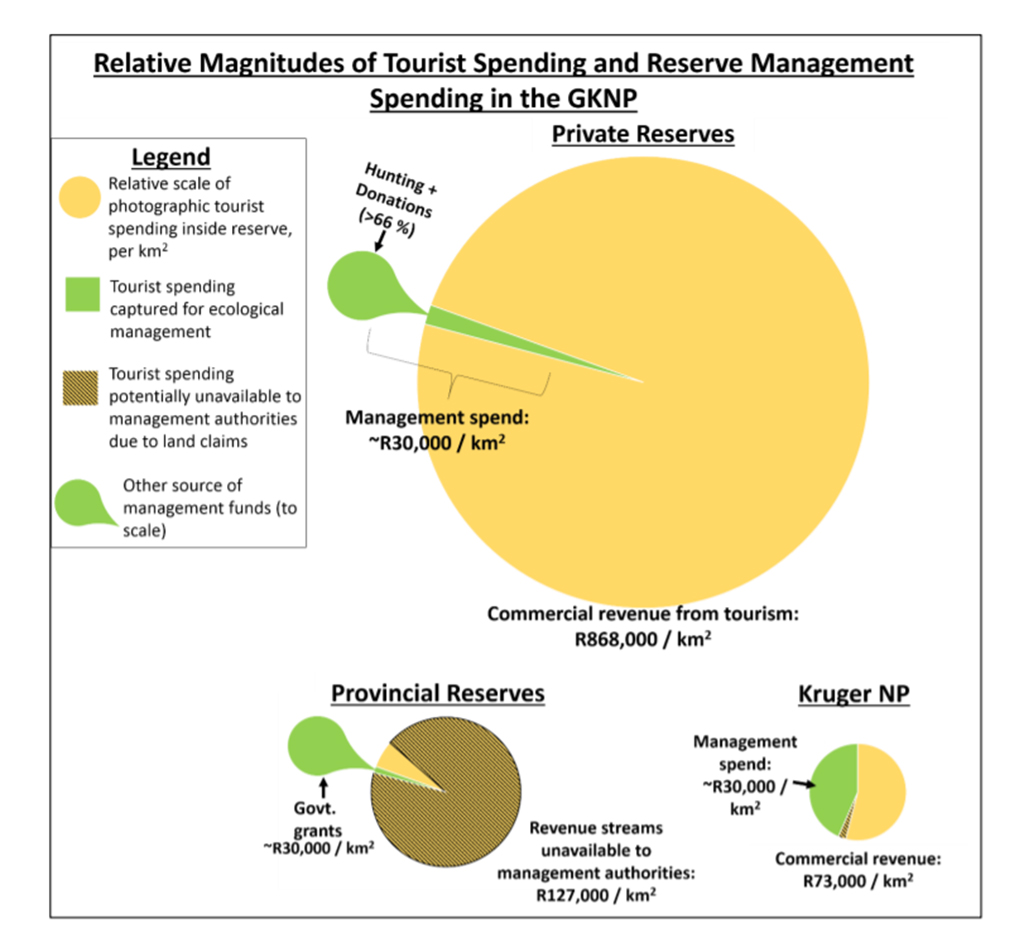
Magnitudes of tourist spending vs management funding
Of the estimated R5.8 billion trip-related spending in South Africa by GKNP photographic tourists, all but R0.9 billion (which went into travel costs) was received in the local area. The total number of people employed in the GKNP equated to around 10,388, with R1.17 billion spent on wages and salaries in one year. In terms of both tourist spending and employment, the surrounding private reserves accounted for the majority. In total, the GKNP contributed R2.6 billion to South Africa’s GDP for 2016/17, including R975 million in tax revenue. When accounting for chain multipliers and induced spending of wage-earners, this contribution could be considered almost tripled to around R6.6 billion to the national economy.
Considered as an overall system, 80% of funding for reserve management of the GKNP is generated by photographic tourism, but this does not apply evenly across the surrounding private reserves. While in the National Park visitor fees go directly into covering conservation costs, the private reserves rely primarily on a levy system charged to commercial operators. The report suggests that resistance to levy hikes has resulted in managers of the private reserves having to seek alternative funds from donors and consumptive tourism. In some of the private reserves, consumptive tourism and trophy hunting account for up to 80% of the management income. In contrast, the provincial reserves are almost entirely reliant on public funds.
Greater Kruger
The presence of the Kruger National Park served as a powerful catalyst for the growth of a large and vibrant economy in the surrounding area, with substantial conservation, social and economic benefits as a result. The provincial reserves, however, are struggling with several challenges including poor infrastructure, high wage bills and low funding, as well as claims by neighbouring communities on the existing revenue streams. These issues, combined with weak governance and a lack of accountability at provincial and community-level could undermine the entire system, say the authors.
The system’s most significant capacity for institutional resilience comes through the diverse functions each component offers, something that will be particularly relevant during the current COVID-19 pandemic (which occurred after the compilation of this article). Importantly, the researchers call for an extended approach in assessing the value of each component of the GKNP and, given that their approach has yielded a much larger economy than previously thought, this needs to be taken into account for high-level strategies. Though the private reserves generate the most revenue, their relationship with the national park is symbiotic; it allows them to capitalize on the brand as a whole, creating a public-private mosaic.
The study concludes that the “partnership in the Greater Kruger National Park between private reserves and the national park is key, not only for branding but for stabilizing the system’s high-performing economic engine with political and cultural ballast.”
Summary Greater Kruger National Park figures for the 2016/17 season
Direct contribution to GDP R 2.6 billion
Total contribution to GDP (including multipliers) R 6.6 billion
Direct tax revenue R 1.0 billion
Total tax revenue (including multipliers) R 1.5 billion
Employment created 10,388 jobs
Wages and salaries R 1.2 billion
Private reserves (±12% land area) ± 60% contribution of revenue and jobs
Total bed nights and day visits 3.5 million
The full report can be accessed here: “The Comparative Financial and Economic Performance of Protected Areas in the Greater Kruger National Park, South Africa: Functional Diversity and Resilience in the Socio-Economics of a Landscape-Scale Reserve Network,” Chidakel, A., Eb, C. and Child, B. (2020) Journal of Sustainable Tourism.
A 2020 study has revealed the considerable economic contributions of the Kruger National Park and the surrounding “contiguous reserves” that together compose the Greater Kruger National Park (GKNP). The study is a joint effort between researchers from the University of Florida and South African National Parks (SANParks).
In considering the public, private, and community-owned components as a whole, the study attributes different values in financial, social, and political domains to each. The researchers suggest that the GKNP should be considered as a whole when working towards management frameworks and policies. The private reserves, while constituting only 12% of the total land area, were responsible for over 60% of the total employment, tax and GDP contributions. Conversely, the Kruger National Park accounts for almost all domestic visits, performing a vital political and social function.
Across the total 22,686km² (23 million hectares) of the entire open system, there are close to 8,000 beds and some 700 different camp and lodge sites. As a general rule, the Kruger National Park itself is oriented towards budget self-catering options, while the private reserves tend to cater to more luxury, high-end safari experiences. For the study, anyone living within 50km of the GKNP boundary fence was considered to be “local”, which equated to approximately 2.9 million people, including many in semi-rural and socio-economically disadvantaged communities. The study reveals that from a period between 2016-2017, there were 3.5 million bed nights and day-visits to the GKNP, of which 35% on average were foreign tourists. As would be expected, the highest visitation by far was to the Kruger National Park itself, while the provincial reserves (Manyeleti Nature Reserve, Letaba Ranch Game Reserve and Makuya Nature Reserve) accounted for only 1% of the total visits.

Magnitudes of tourist spending vs management funding
Of the estimated R5.8 billion trip-related spending in South Africa by GKNP photographic tourists, all but R0.9 billion (which went into travel costs) was received in the local area. The total number of people employed in the GKNP equated to around 10,388, with R1.17 billion spent on wages and salaries in one year. In terms of both tourist spending and employment, the surrounding private reserves accounted for the majority. In total, the GKNP contributed R2.6 billion to South Africa’s GDP for 2016/17, including R975 million in tax revenue. When accounting for chain multipliers and induced spending of wage-earners, this contribution could be considered almost tripled to around R6.6 billion to the national economy.
Considered as an overall system, 80% of funding for reserve management of the GKNP is generated by photographic tourism, but this does not apply evenly across the surrounding private reserves. While in the National Park visitor fees go directly into covering conservation costs, the private reserves rely primarily on a levy system charged to commercial operators. The report suggests that resistance to levy hikes has resulted in managers of the private reserves having to seek alternative funds from donors and consumptive tourism. In some of the private reserves, consumptive tourism and trophy hunting account for up to 80% of the management income. In contrast, the provincial reserves are almost entirely reliant on public funds.

Greater Kruger
The presence of the Kruger National Park served as a powerful catalyst for the growth of a large and vibrant economy in the surrounding area, with substantial conservation, social and economic benefits as a result. The provincial reserves, however, are struggling with several challenges including poor infrastructure, high wage bills and low funding, as well as claims by neighbouring communities on the existing revenue streams. These issues, combined with weak governance and a lack of accountability at provincial and community-level could undermine the entire system, say the authors.
The system’s most significant capacity for institutional resilience comes through the diverse functions each component offers, something that will be particularly relevant during the current COVID-19 pandemic (which occurred after the compilation of this article). Importantly, the researchers call for an extended approach in assessing the value of each component of the GKNP and, given that their approach has yielded a much larger economy than previously thought, this needs to be taken into account for high-level strategies. Though the private reserves generate the most revenue, their relationship with the national park is symbiotic; it allows them to capitalize on the brand as a whole, creating a public-private mosaic.
The study concludes that the “partnership in the Greater Kruger National Park between private reserves and the national park is key, not only for branding but for stabilizing the system’s high-performing economic engine with political and cultural ballast.”
Summary Greater Kruger National Park figures for the 2016/17 season
Direct contribution to GDP R 2.6 billion
Total contribution to GDP (including multipliers) R 6.6 billion
Direct tax revenue R 1.0 billion
Total tax revenue (including multipliers) R 1.5 billion
Employment created 10,388 jobs
Wages and salaries R 1.2 billion
Private reserves (±12% land area) ± 60% contribution of revenue and jobs
Total bed nights and day visits 3.5 million
The full report can be accessed here: “The Comparative Financial and Economic Performance of Protected Areas in the Greater Kruger National Park, South Africa: Functional Diversity and Resilience in the Socio-Economics of a Landscape-Scale Reserve Network,” Chidakel, A., Eb, C. and Child, B. (2020) Journal of Sustainable Tourism.
