Order: Columbiformes. Family: Columbidae
Description
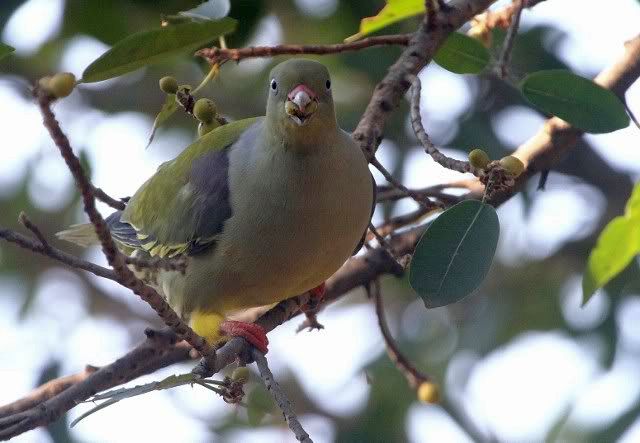
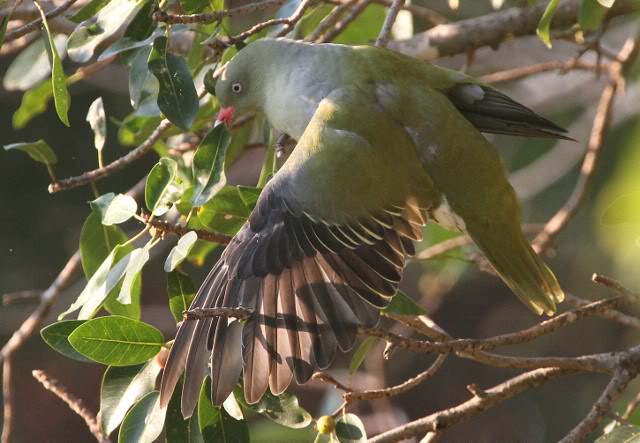
The tambourine dove is a small plump pigeon, typically 22 cm in length. The white face and underparts of male are diagnostic. The tambourine dove’s flight is fast and agile, and it tends to stay quite low when flushed. In flight it shows chestnut primary flight feathers and under wings.
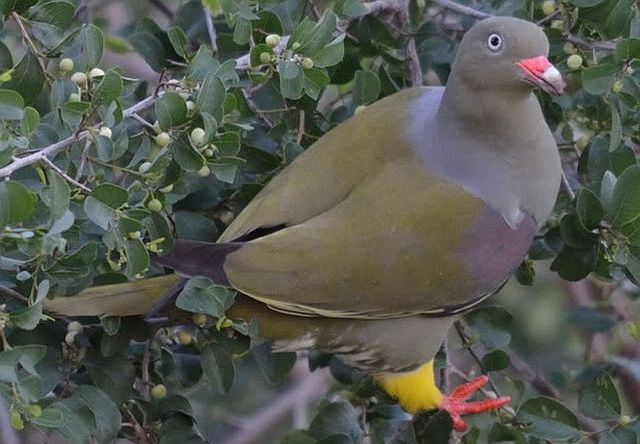
Adult male: Forehead and area around eyes white, loral stripe black. Hind crown, ear coverts, nape and back ashy brown; lower back crossed by 2 indistinct blackish bands, with paler band between. Central pair of rectrices dark reddish brown; 2 outer pairs ashy, with subterminal dark grey to black bar. Remainder basally dark brown, distal third blackish. Upper wing coverts brown. Primaries and outer secondaries cinnamon, edged and tipped brown. Central and inner secondaries brown; 2 iridescent blackish-purple spots on wing formed by metallic markings on some inner coverts and secondaries. Underwing cinnamon. Throat to vent white; undertail coverts and flanks ashy brown. Bill purplish, tipped dark brown or black. Eyes brown. Legs and feet reddish purple.
Adult female: As male, but with lower throat and breast washed grey.
The juvenile resembles the female but has chestnut fringes to the feathers of the back, breast and flanks. Brown above, most feathers transversely barred rufous and brown; breast grey in both sexes. Even in these plumages, this species is paler below than other small African doves.
Distribution
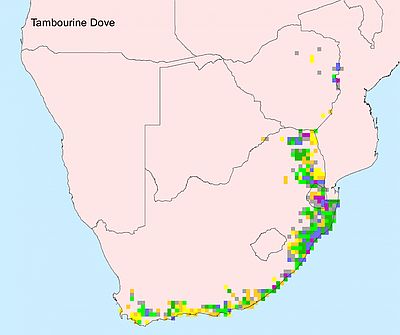
Occurs across sub-Saharan Africa, excluding arid areas. Its range extends from Senegal east to Ethiopia and Kenya and southwards through eastern Africa to south-eastern South Africa, but it is absent from the drier areas of south-western Africa. There is a population on the Comoros Islands. It is locally common in Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Swaziland, the Limpopo province and large areas of the east coast of South Africa, from KwaZulu-Natal to the Western Cape.
Habitat
The tambourine dove (Turtur tympanistria) is a pigeon which is a widespread resident breeding bird in woodlands and other thick vegetation in Africa south of the Sahara Desert. It generally prefers riverine woodland and evergreen forest, often occupying coastal forest in the Western and Eastern Cape.
Diet
It eats a variety of fruit, seeds and invertebrates, usually foraging on the ground.
Breeding
Both sexes construct the nest, which is a fragile saucer made of twigs, leaves and petioles. The male collects material and hands it to the female, who then incorporates it to the structure. It is typically placed among the tangled branches of a creeper, in a bush or tree, often in vegetation next to rivers. Egg-laying season is from about September-May. It lays 1-2 cream-coloured eggs, which are incubated mainly by the female for about 17-20 days. The chicks are fed about four times daily by both parents, who regurgitate food eaten previously. They are brooded constantly for the first few days of their lives, staying in the nest for about 19-22 days.
Call
The call of this bird is a persistently repeated du-du-du-du-du.
Status
Fairly common resident. It is usually solitary, but is sometimes seen in family groups or with lemon doves.



 © Peter Connan
© Peter Connan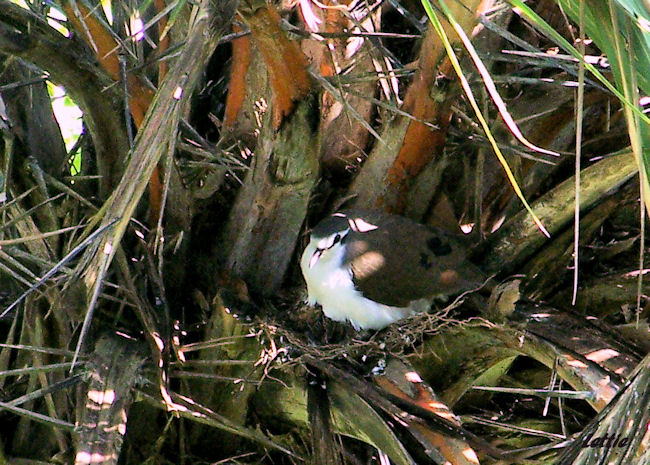 © 100ponder
© 100ponder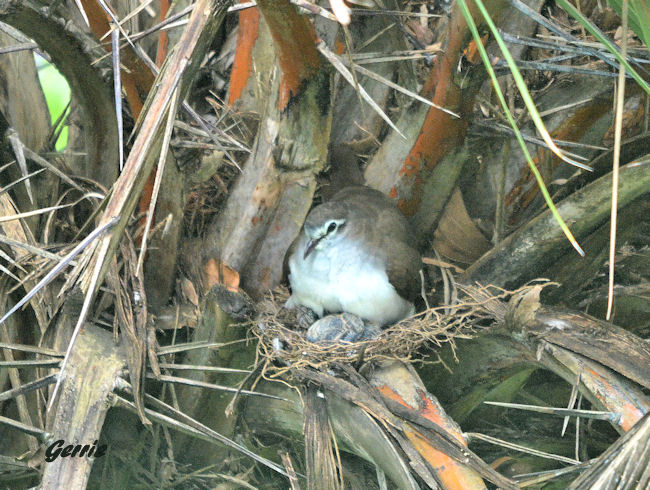 © 100ponder
© 100ponder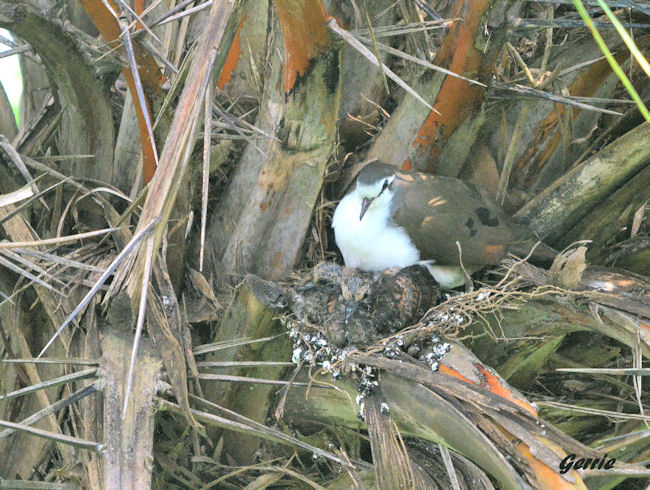 © 100ponder
© 100ponder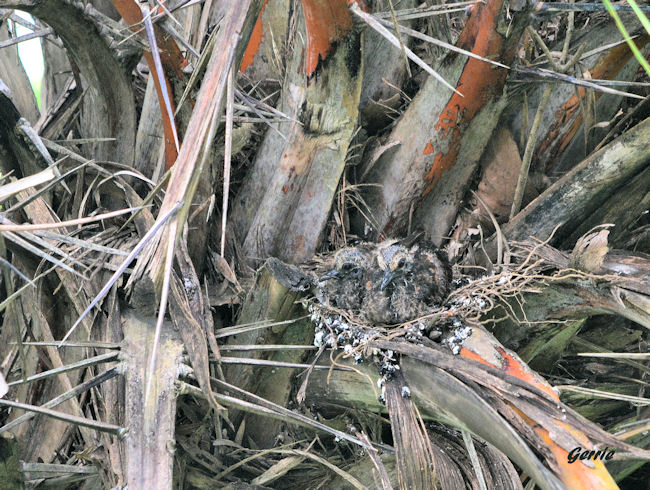 © 100ponder
© 100ponder
 © Toko
© Toko © BluTuna
© BluTuna © Pumbaa
© Pumbaa © leachy
© leachy © Dewi
© Dewi © Mel
© Mel © Dewi
© Dewi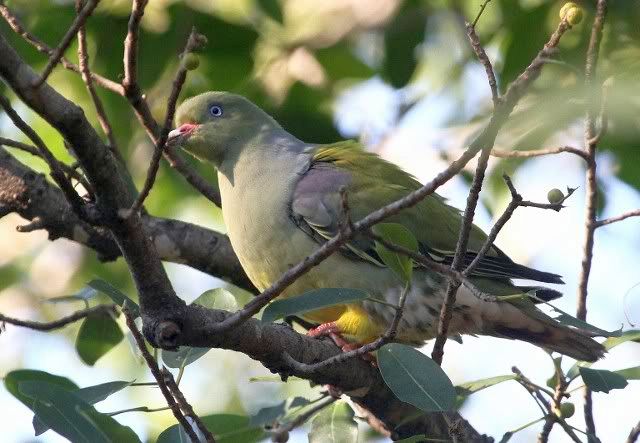

 © BluTuna
© BluTuna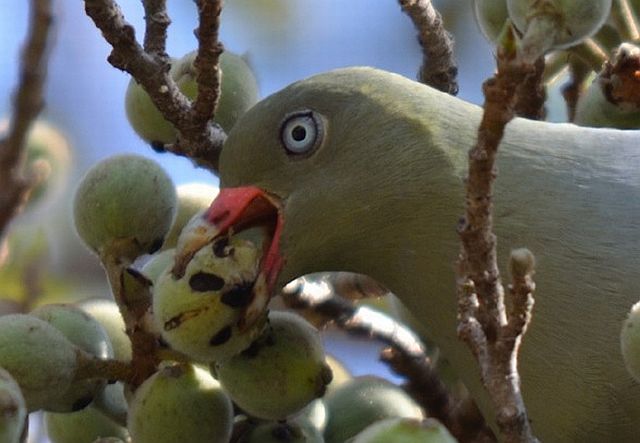 © BluTuna
© BluTuna  © Bushcraft
© Bushcraft
 © Duke
© Duke © Duke
© Duke © Duke
© Duke