834. Green-winged Pytilia (formerly known as Melba Finch) Pytilia melba (Gewone Melba)
Order: Passeriformes. Family: Estrildidae
Description
The Green-winged Pytilia has a height of 13 cm. Both sexes have orange-red bills and grey-brown legs and feet.
Adult male: Frons, forecrown and cheeks scarlet; hind crown, lores, remainder of face and nape grey. Mantle, back and rump yellowish olive green; upper tail coverts red. Central rectrices reddish, remainder grey-brown, washed red, especially on outer edges. Upper wing coverts yellowish olive green. Flight feathers grey-brown, edged yellowish olive green. Throat scarlet. Upper breast greenish gold; remainder of underparts barred grey and white, centre of belly and undertail coverts more diffuse and buffy. Bill orange-red, non-br male with ridge dark horn. Eyes reddish orange, red-brown or scarlet; eye ring pale grey, narrow. Legs and feet pinkish to greyish brown.
The grey (not red) ear coverts and olive green (not orange) wings separate it from Orange-winged Pytilia (833.).
The female lacks the red on the head, the entire head being grey, and the throat and breast are white barred with black, olive green wings.
The juvenile's head and throat are olive; it is plain greyish below and has a black bill.
Distribution: It occurs across much of sub-Saharan Africa excluding the lowland forest of the West African coast, from Senegal to southern Sudan and Somalia south to Zambia, Angola, Malawi and southern Africa. Here it is common from Mozambique and northern and eastern South Africa to Zimbabwe, Botswana (excluding the arid Kalahari) and northern Namibia.
Habitat
It generally prefers thickets and rank clumps of grass in dry woodland, especially with Acacia trees, while in more arid areas it favours edges of drainage lines and riverine woodland, since it is dependent on surface water being available.
Diet
It feeds mainly on seeds and insects especially termites. It forages in low bushy vegetation and in clearings on the ground.
Breeding
Green-winged Pytilias are monogamous and build a nest that is an untidy ball of dry grass with a side entrance, and is generally located in a thorny bush just one to two metres above the ground. Egg-laying season is year-round, peaking from January-May. It lays 2-5, rarely 6 white eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for about 12-14 days. The chicks are brooded and fed by both parents, leaving the nest after about 18-21 days.
The nest may be parasitized by the Long-tailed Paradise Whydah.
Call
2-3 water droplet sounds followed by trill prrreeeeeoooo. Listen to Bird Call.
Status
Common resident.
Africa Wild Bird Book
Green-winged Pytilia Photos
834. Green-winged Pytilia (formerly known as Melba Finch) Pytilia melba
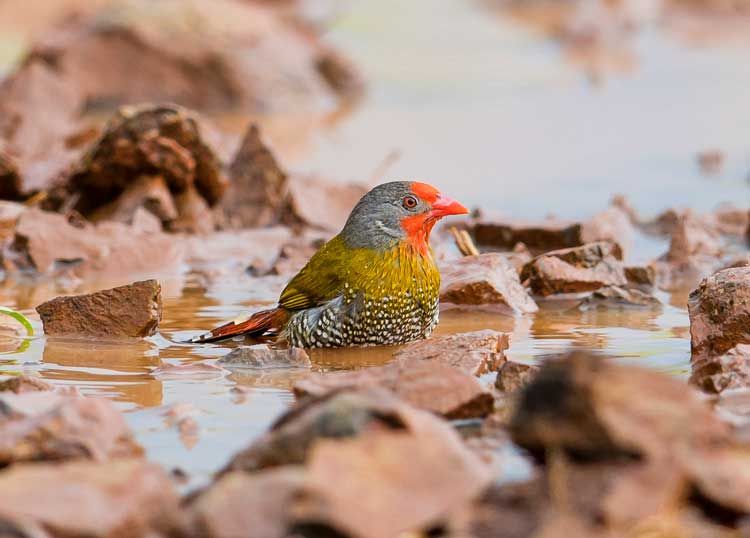 © Pumbaa
© Pumbaa
Kruger National Park, S28
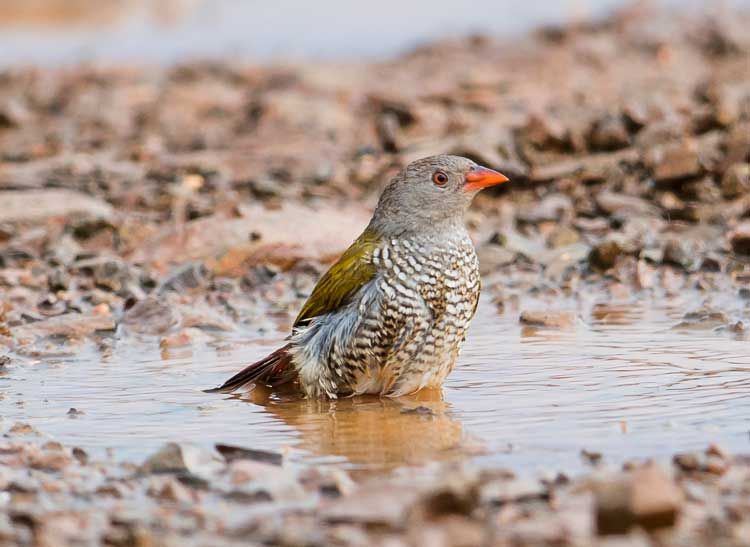 © Pumbaa
© Pumbaa
Kruger National Park, S28
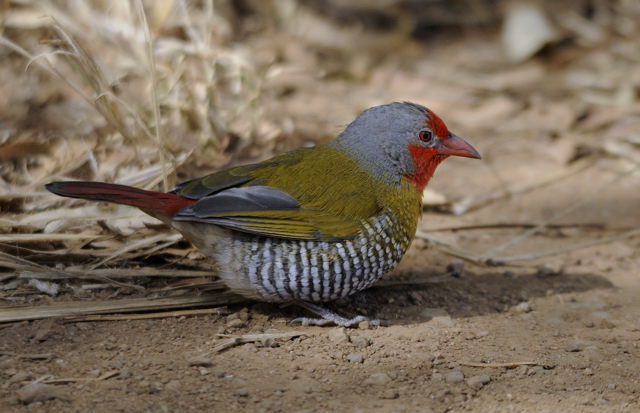 © Dewi
© Dewi
Male
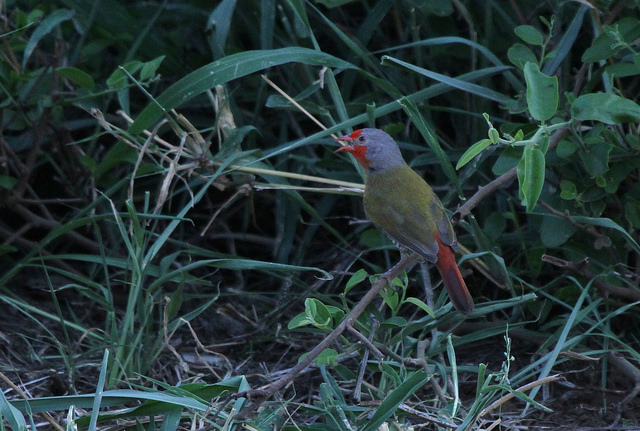 © flying cheetah
© flying cheetah
Kruger National Park, S56 Mphongolo Road
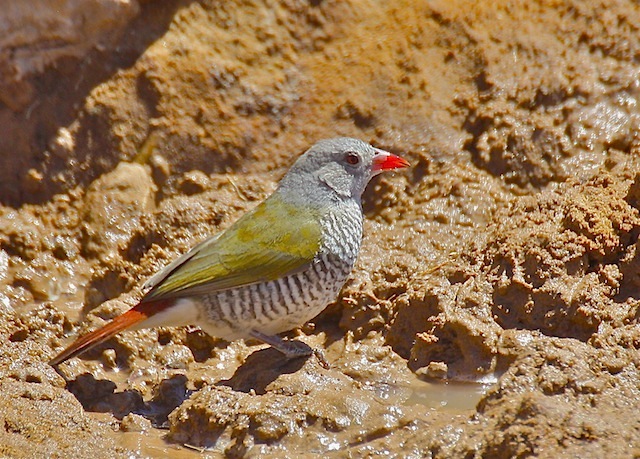 © ExFmem
© ExFmem
Female
Links:
Species text Sabap1
Sabap2
 © Pumbaa
© PumbaaKruger National Park, S28
 © Pumbaa
© PumbaaKruger National Park, S28
 © Dewi
© DewiMale
 © flying cheetah
© flying cheetahKruger National Park, S56 Mphongolo Road
 © ExFmem
© ExFmemFemale
Links:
Species text Sabap1
Sabap2
- Flutterby
- Posts: 44029
- Joined: Sat May 19, 2012 12:28 pm
- Country: South Africa
- Location: Gauteng, South Africa
- Contact:
Red-headed Finch
856. Red-headed Finch Amadina erythrocephala (Rooikopvink)
Order: Passeriformes. Family: Estrildidae
Description
Length 13 cm; bill very heavy; tail rounded. The upperpart of this species are generally brown, and the underparts are pale and heavy scalloped.
Adult male: Bright red head; rest of upperparts greyish brown, faintly barred on rump; breast and flanks fawn, spotted with white, each spot outlined in black; lower belly white; undertail barred black, white and brown.
Adult female: Similar to male, but head brown above, barred black and white on throat.
Juvenile is duller than adult.
Similar species: Red-headed Quela is similar but has plain underparts. Female differs from the smaller female Cut-throat Finch in having a uniformly pale brown head, and less heavily barred and streaked underparts and upperparts.
Distribution
Near-endemic to southern Africa, occurring from south-western Zimbabwe through Botswana and much of South Africa to Namibia and south-western Angola.
Habitat
Arid and semi-arid grassland, shrublands and savanna.
Diet
The Red-headed finch forages for seeds and insects mainly on the ground.
Breeding
Monogamous. The Red-headed-finch seldom builds its own nest and commonly nests in the old nests of one of the Ploceus weavers. The nest can be either a small pad or a ball, made of grass and lined with feathers. It is typically placed in an old nest of another bird, such as a Ploceus weaver, Red-billed buffalo weaver, Cape sparrow or a Sociable weaver, although it may occasionally use a hole in a tree or building instead. It can breed at any time of year in response to rainfall, but egg-laying season is usually from February-September. It lays 2-11, usually 4-6 white eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for about 12-14 days. The chicks are fed by both parents, leaving the nest after about 15-21 days.
Call
A soft chuk-chuk-chuk, and a zree, zree flight call. and it also makes a variety of whirring or buzzing sounds. Listen to Bird Call.
Status
Common resident and nomad; near-endemic; usually in flocks and nomadic in non-breeding season.
Order: Passeriformes. Family: Estrildidae
Description
Length 13 cm; bill very heavy; tail rounded. The upperpart of this species are generally brown, and the underparts are pale and heavy scalloped.
Adult male: Bright red head; rest of upperparts greyish brown, faintly barred on rump; breast and flanks fawn, spotted with white, each spot outlined in black; lower belly white; undertail barred black, white and brown.
Adult female: Similar to male, but head brown above, barred black and white on throat.
Juvenile is duller than adult.
Similar species: Red-headed Quela is similar but has plain underparts. Female differs from the smaller female Cut-throat Finch in having a uniformly pale brown head, and less heavily barred and streaked underparts and upperparts.
Distribution
Near-endemic to southern Africa, occurring from south-western Zimbabwe through Botswana and much of South Africa to Namibia and south-western Angola.
Habitat
Arid and semi-arid grassland, shrublands and savanna.
Diet
The Red-headed finch forages for seeds and insects mainly on the ground.
Breeding
Monogamous. The Red-headed-finch seldom builds its own nest and commonly nests in the old nests of one of the Ploceus weavers. The nest can be either a small pad or a ball, made of grass and lined with feathers. It is typically placed in an old nest of another bird, such as a Ploceus weaver, Red-billed buffalo weaver, Cape sparrow or a Sociable weaver, although it may occasionally use a hole in a tree or building instead. It can breed at any time of year in response to rainfall, but egg-laying season is usually from February-September. It lays 2-11, usually 4-6 white eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for about 12-14 days. The chicks are fed by both parents, leaving the nest after about 15-21 days.
Call
A soft chuk-chuk-chuk, and a zree, zree flight call. and it also makes a variety of whirring or buzzing sounds. Listen to Bird Call.
Status
Common resident and nomad; near-endemic; usually in flocks and nomadic in non-breeding season.
- Flutterby
- Posts: 44029
- Joined: Sat May 19, 2012 12:28 pm
- Country: South Africa
- Location: Gauteng, South Africa
- Contact:
Red-headed Finch Photos
856. Red-headed Finch Amadina erythrocephala
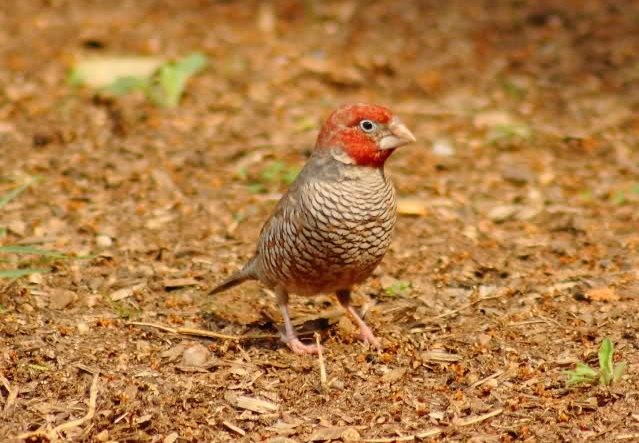 © Flutterby
© Flutterby
Male
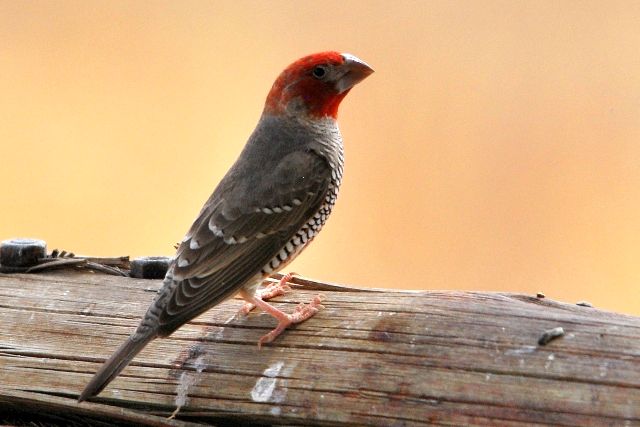 © Mel
© Mel
Male
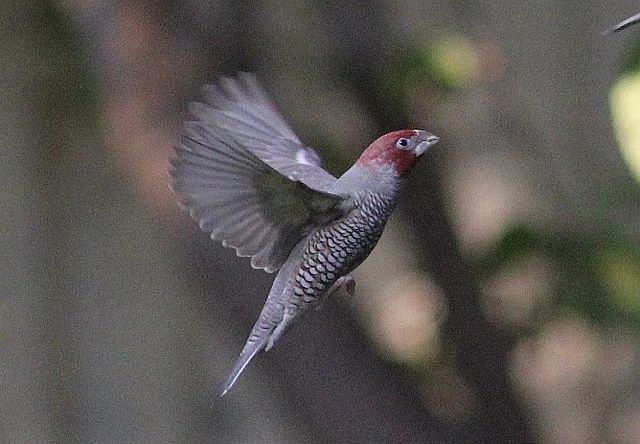 © Amoli
© Amoli
Male
 © Sharifa & Duke
© Sharifa & Duke
Males
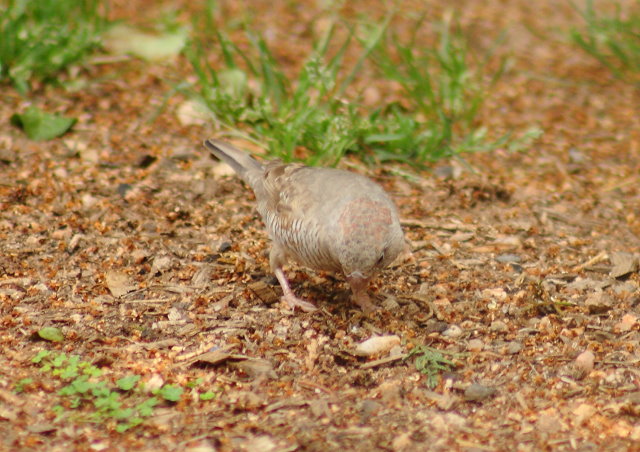 © Flutterby
© Flutterby
Female
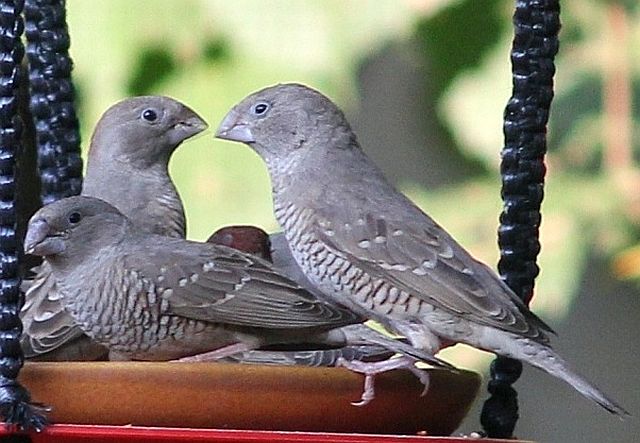 © Amoli
© Amoli
Females
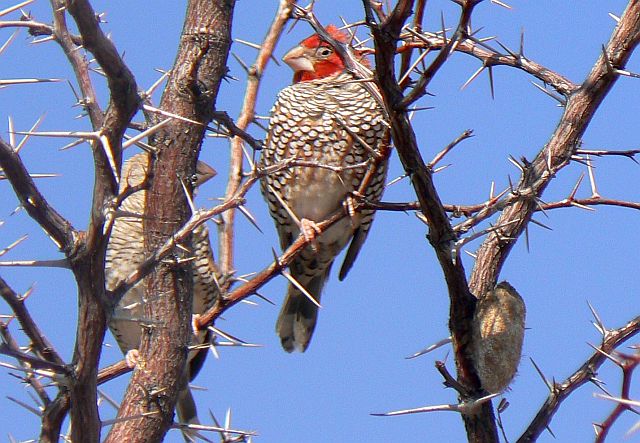 © Toko
© Toko
Female & Male
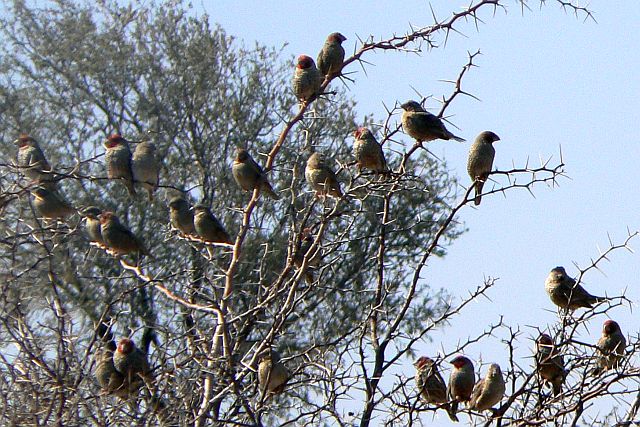 © Toko
© Toko
Red-headed Finches may be found in large flocks of up to hundreds of birds.
Links:
Species text Sabap1
Sabap2
Sasol
 © Flutterby
© FlutterbyMale
 © Mel
© MelMale
 © Amoli
© AmoliMale
 © Sharifa & Duke
© Sharifa & DukeMales
 © Flutterby
© FlutterbyFemale
 © Amoli
© AmoliFemales
 © Toko
© TokoFemale & Male
 © Toko
© TokoRed-headed Finches may be found in large flocks of up to hundreds of birds.
Links:
Species text Sabap1
Sabap2
Sasol
- nan
- Posts: 26476
- Joined: Thu May 31, 2012 9:41 pm
- Country: Switzerland
- Location: Central Europe
- Contact:
Cut-throat Finch
855. Cut-throat Finch Amadina fasciata (Bandkeelvink)
Order: Passeriformes. Family: Estrildidae
Description
Size 10-11 cm. The plumage is generally brown, heavily barred and mottled with black and white. The legs are a pink fleshy colour.
Adult male: The pinkish, red band across the throat is diagnostic in male. Upperparts are brown with fine black bars; wing bar formed by a dark band and pale tip on the greater and median wing-coverts. The chin is white, bordered by a red throat band that extends to the ear coverts.
Adult female: Similar to the male, but without the red "cut-throat" marking, pale bill. The female is smaller than male Red-headed Finch, is boldly barred on the head, and has the back distinctly streaked and mottled.
The juvenile resembles female, but juvenile male shows a pale throat band.
Distribution
Occurs across the Sahel from Senegal to Ethiopia south to Kenya and Tanzania, with a separate population in the area from southern Angola, Zambia and Malawi to southern Africa. Here it is uncommon to fairly common from localised parts of Mozambique through Zimbabwe to Botswana and north-eastern South Africa, while scarce in Namibia.
Habitat
Dry thornveld.
Diet
It does most of its foraging on the ground, mainly feeding on seeds and termites.
Breeding
Monogamous. The nest is built by both sexes, consisting of a ball of grass with a short entrance tunnel, while the interior is lined with feathers. It is typically placed in the old nest of a Ploceus weaver, Red-billed buffalo Weaver, Red-headed Weaver or woodpecker, rarely using a hole in a fence post instead. Egg-laying season is year-round, peaking from December-April. It lays 2-7, usually 4-6 white eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for about 12-13 days. The chicks leave the nest after about 21-23 days.
Call
An eee-eee-eee flight call. Listen to Bird Call.
Status
Locally common resident.
Order: Passeriformes. Family: Estrildidae
Description
Size 10-11 cm. The plumage is generally brown, heavily barred and mottled with black and white. The legs are a pink fleshy colour.
Adult male: The pinkish, red band across the throat is diagnostic in male. Upperparts are brown with fine black bars; wing bar formed by a dark band and pale tip on the greater and median wing-coverts. The chin is white, bordered by a red throat band that extends to the ear coverts.
Adult female: Similar to the male, but without the red "cut-throat" marking, pale bill. The female is smaller than male Red-headed Finch, is boldly barred on the head, and has the back distinctly streaked and mottled.
The juvenile resembles female, but juvenile male shows a pale throat band.
Distribution
Occurs across the Sahel from Senegal to Ethiopia south to Kenya and Tanzania, with a separate population in the area from southern Angola, Zambia and Malawi to southern Africa. Here it is uncommon to fairly common from localised parts of Mozambique through Zimbabwe to Botswana and north-eastern South Africa, while scarce in Namibia.
Habitat
Dry thornveld.
Diet
It does most of its foraging on the ground, mainly feeding on seeds and termites.
Breeding
Monogamous. The nest is built by both sexes, consisting of a ball of grass with a short entrance tunnel, while the interior is lined with feathers. It is typically placed in the old nest of a Ploceus weaver, Red-billed buffalo Weaver, Red-headed Weaver or woodpecker, rarely using a hole in a fence post instead. Egg-laying season is year-round, peaking from December-April. It lays 2-7, usually 4-6 white eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for about 12-13 days. The chicks leave the nest after about 21-23 days.
Call
An eee-eee-eee flight call. Listen to Bird Call.
Status
Locally common resident.
Kgalagadi lover… for ever
https://safrounet.piwigo.com/
https://safrounet.piwigo.com/
- nan
- Posts: 26476
- Joined: Thu May 31, 2012 9:41 pm
- Country: Switzerland
- Location: Central Europe
- Contact:
Cut-throat Finch Photos
855. Cut-throat Finch Amadina fasciata
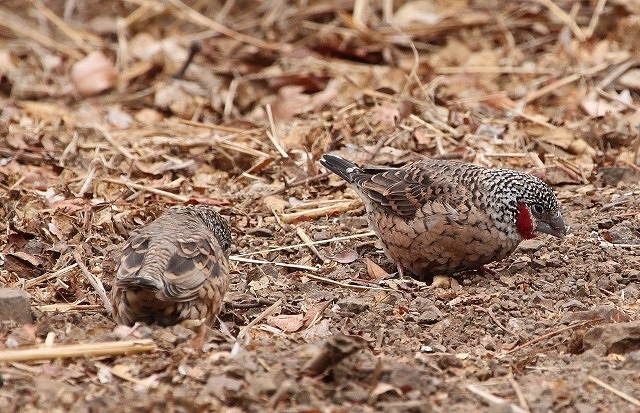 © nan
© nan
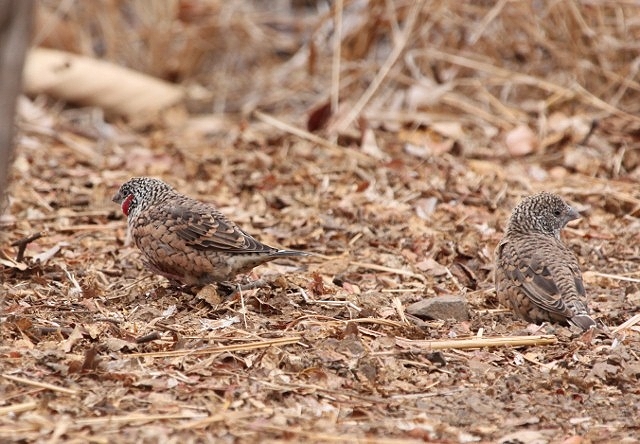 © nan
© nan
Male & female
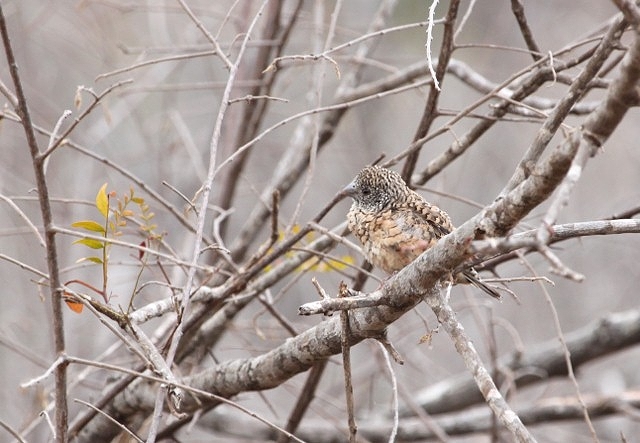 © nan
© nan
Female
 © Michele Nel
© Michele Nel
Red Rocks, Kruger National Park
Links:
Species Text Sabap1
Sabap2
 © nan
© nan © nan
© nanMale & female
 © nan
© nanFemale
 © Michele Nel
© Michele NelRed Rocks, Kruger National Park
Links:
Species Text Sabap1
Sabap2
Kgalagadi lover… for ever
https://safrounet.piwigo.com/
https://safrounet.piwigo.com/
Green Twinspot
835. Green Twinspot, Green-backed Twinspot Mandingoa nitidula (Groenkolpensie)
Order: Passeriformes. Family: Estrildidae
Description
Small (10-11 cm), with short tail. Olive green above with white-spotted black belly; throat and breast golden olive; rump dull orange. Undertail olive grey. Face patch is red in the male and yellow in the female. Iris brown; bill black, tip orange; legs and feet pinkish brown.
Male nominate race has area from lores to behind eye and to chin red, crown, upperparts, upperwing and tail olive-green.
Females have a buff face and chin.
Juvenile: Duller than adult; below greyish olive without spots; face and chin buff; may breed in this plumage; adult plumage acquired at about 3 months.
Chick: Gape papillae blue.
Similar species: No other twinspot has green upperparts, and all are generally much darker.
Taxonomy
Mandingoa nitidula has four subspecies:
M. n. schlegeli: Sierra Leone to Angola, DR Congo, and Uganda.
M. n. virginiae: Gulf of Guinea Islands: Bioko.
M. n. chubbi: Southern Ethiopia to north-eastern Zambia, northern Malawi and northern Mozambique.
M. n. nitidula: DR Congo, north-western Zambia, southern Malawi and northern and central Mozambique to South Africa.
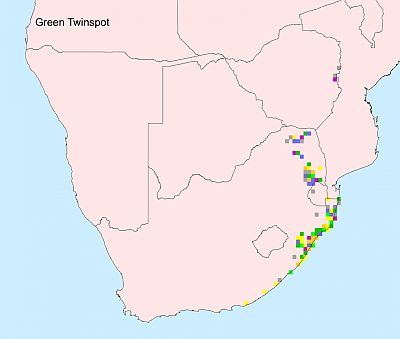
Distribution
It occurs in patches of sub-Saharan Africa, from West Africa to much of the DRC and surrounding countries, extending south to southern Africa. Here it is uncommon to locally common in Zimbabwe's eastern highlands and adjacent central Mozambique, with a separate population in eastern South Africa and Swaziland, from Limpopo province to KwaZulu-Natal and marginally in the Eastern Cape.
Habitat
It generally prefers edges of forest, especially with tangled bracken-brier scrub or gardens, also occupying alien tree plantations, particularly with patches of Ribbon Bristle Grass (Setaria chevalieri).
Diet
It mainly eats seeds taken from the ground or directly from plants, especially grasses, supplemented with small insects.
Breeding
The nest is built by both sexes, consisting of a bulk oval ball with a small entrance spout, made of grass stems, skeletonised leaves, rootlets, twigs and old-man's-beard lichen (Usnea) and lined with feathers, fine grass and other soft material. It is typically concealed in the canopy of a tall tree, but it may rarely use an abandoned Dark-backed Weaver nest instead of building its own. Egg-laying season is from December to April in KwaZulu-Natal. The female lays 4-6 white eggs, which are incubated by both parents for about 12-14 days. The chicks are fed by both parents, leaving the nest after about 17 days and becoming independent about a week later.
Call
Contact call a chirping tzeeet, alarm a low dzzhurrrr. Song a series of tik and whistled notes, variable, chrrr tik tik tik cheer weet weet weet teeu wooee tseeeu.
Status
Localised fairly common resident.
Order: Passeriformes. Family: Estrildidae
Description
Small (10-11 cm), with short tail. Olive green above with white-spotted black belly; throat and breast golden olive; rump dull orange. Undertail olive grey. Face patch is red in the male and yellow in the female. Iris brown; bill black, tip orange; legs and feet pinkish brown.
Male nominate race has area from lores to behind eye and to chin red, crown, upperparts, upperwing and tail olive-green.
Females have a buff face and chin.
Juvenile: Duller than adult; below greyish olive without spots; face and chin buff; may breed in this plumage; adult plumage acquired at about 3 months.
Chick: Gape papillae blue.
Similar species: No other twinspot has green upperparts, and all are generally much darker.
Taxonomy
Mandingoa nitidula has four subspecies:
M. n. schlegeli: Sierra Leone to Angola, DR Congo, and Uganda.
M. n. virginiae: Gulf of Guinea Islands: Bioko.
M. n. chubbi: Southern Ethiopia to north-eastern Zambia, northern Malawi and northern Mozambique.
M. n. nitidula: DR Congo, north-western Zambia, southern Malawi and northern and central Mozambique to South Africa.
Distribution
It occurs in patches of sub-Saharan Africa, from West Africa to much of the DRC and surrounding countries, extending south to southern Africa. Here it is uncommon to locally common in Zimbabwe's eastern highlands and adjacent central Mozambique, with a separate population in eastern South Africa and Swaziland, from Limpopo province to KwaZulu-Natal and marginally in the Eastern Cape.

Habitat
It generally prefers edges of forest, especially with tangled bracken-brier scrub or gardens, also occupying alien tree plantations, particularly with patches of Ribbon Bristle Grass (Setaria chevalieri).
Diet
It mainly eats seeds taken from the ground or directly from plants, especially grasses, supplemented with small insects.
Breeding
The nest is built by both sexes, consisting of a bulk oval ball with a small entrance spout, made of grass stems, skeletonised leaves, rootlets, twigs and old-man's-beard lichen (Usnea) and lined with feathers, fine grass and other soft material. It is typically concealed in the canopy of a tall tree, but it may rarely use an abandoned Dark-backed Weaver nest instead of building its own. Egg-laying season is from December to April in KwaZulu-Natal. The female lays 4-6 white eggs, which are incubated by both parents for about 12-14 days. The chicks are fed by both parents, leaving the nest after about 17 days and becoming independent about a week later.
Call
Contact call a chirping tzeeet, alarm a low dzzhurrrr. Song a series of tik and whistled notes, variable, chrrr tik tik tik cheer weet weet weet teeu wooee tseeeu.
Status
Localised fairly common resident.
Green Twinspot Photos
835. Green Twinspot, Green-backed Twinspot Mandingoa nitidula
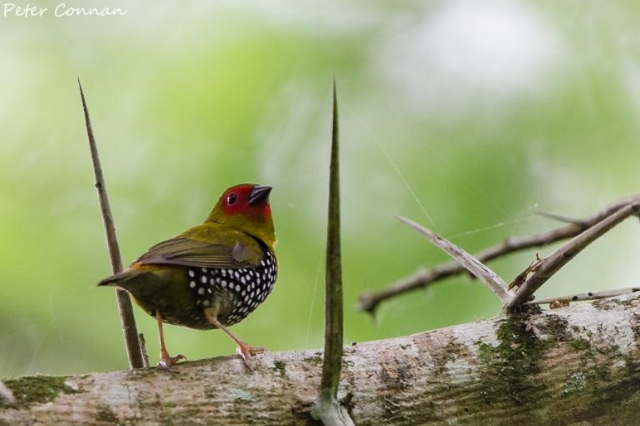 © Peter Connan
© Peter Connan
Male, Maphelane, iSimangaliso Wetland Park, KwaZulu-Natal
Links:
Sabap1 Species text in The Atlas of Southern African Birds
Sabap2
Finches and Sparrows. Peter Clement
 © Peter Connan
© Peter ConnanMale, Maphelane, iSimangaliso Wetland Park, KwaZulu-Natal
Links:
Sabap1 Species text in The Atlas of Southern African Birds
Sabap2
Finches and Sparrows. Peter Clement
Pink-throated Twinspot
838. Pink-throated Twinspot Hypargos margaritatus (Rooskeelkopensie)
Order: Passeriformes. Family: Estrildidae
Description
12 cm.
Male has brown upperparts brown, except for the upper tail coverts which are deep pink. The face, throat and upper breast are also deep pink. The remainder of the underparts are black with white spots. Bill is pale blue. The legs, and feet are dark. The eyes are dark brown with a narrow pale pinkish-blue eye-ring.
Female is grey on the face, breast and belly, has only rump and tail pink.
Habitat
Dense, tangled thickets in thornveld, sandforest and coastal thickets.
Distribution
Endemic to southern Africa, restricted to southern Mozambique, eastern Swaziland, north-eastern KwaZulu-Natal, and marginally eastern Mpumalanga, with an isolated population in northern Limpopo Province.
Diet
It mainly eats seeds of grasses.
Breeding
The nest is an untidy ball with a side entrance, made dry grass or leaf ribs, skeletonised leaves, inflorescences and spider webs, lined with palm fibres and leaf litter. It is typically concealed in dense vegetation and leaf litter, less than one metre above ground.
Call
Song: 2-6 flute-like whistles; call includes trills. Listen to Bird Call.
Status
Locally common resident; endemic.
Order: Passeriformes. Family: Estrildidae
Description
12 cm.
Male has brown upperparts brown, except for the upper tail coverts which are deep pink. The face, throat and upper breast are also deep pink. The remainder of the underparts are black with white spots. Bill is pale blue. The legs, and feet are dark. The eyes are dark brown with a narrow pale pinkish-blue eye-ring.
Female is grey on the face, breast and belly, has only rump and tail pink.
Habitat
Dense, tangled thickets in thornveld, sandforest and coastal thickets.
Distribution
Endemic to southern Africa, restricted to southern Mozambique, eastern Swaziland, north-eastern KwaZulu-Natal, and marginally eastern Mpumalanga, with an isolated population in northern Limpopo Province.
Diet
It mainly eats seeds of grasses.
Breeding
The nest is an untidy ball with a side entrance, made dry grass or leaf ribs, skeletonised leaves, inflorescences and spider webs, lined with palm fibres and leaf litter. It is typically concealed in dense vegetation and leaf litter, less than one metre above ground.
Call
Song: 2-6 flute-like whistles; call includes trills. Listen to Bird Call.
Status
Locally common resident; endemic.
Dewi
What is the good of having a nice house without a decent planet to put it on? (H D Thoreau)
What is the good of having a nice house without a decent planet to put it on? (H D Thoreau)
Pink-throated Twinspot Photos
838. Pink-throated Twinspot Hypargos margaritatus (Rooskeelkopensie)
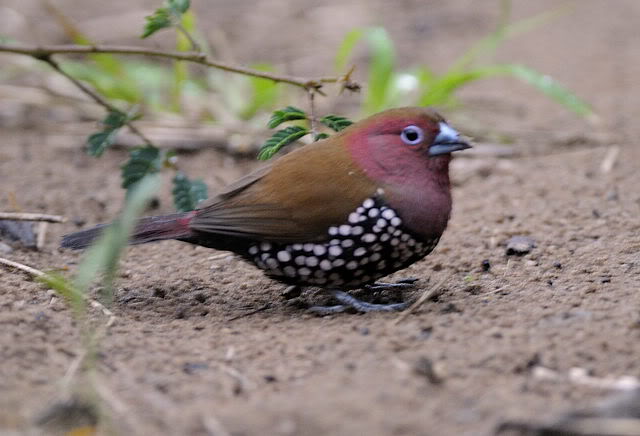

Male
Links:
Species text Sabap1
Sabap2
Ian Sinclair. SASOL VOELS VAN SUIDER AFRICA (3de UIT)

Male
Links:
Species text Sabap1
Sabap2
Ian Sinclair. SASOL VOELS VAN SUIDER AFRICA (3de UIT)
Dewi
What is the good of having a nice house without a decent planet to put it on? (H D Thoreau)
What is the good of having a nice house without a decent planet to put it on? (H D Thoreau)


