Order: Passeriformes. Family: Estrildidae
Description
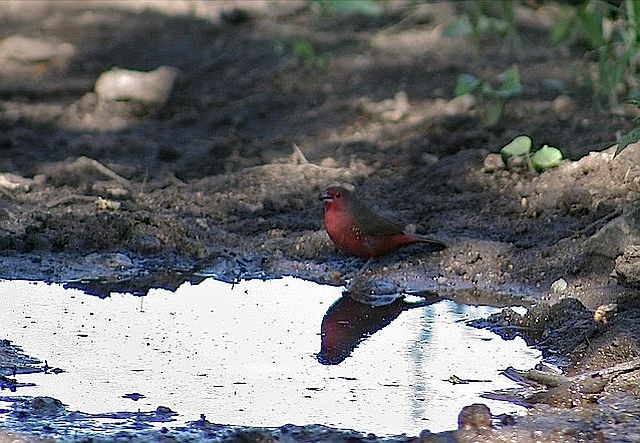
Size 9-10 cm. Only firefinch in region with combination of pinkish bill and red rump. The pink and bright bill, pale yellow eye-ring are diagnostic in both sexes. Iris brown and eye rims yellow. Distinquished from other Firefinches by reddish bill or, in mixed parties, by the grey-brown females.
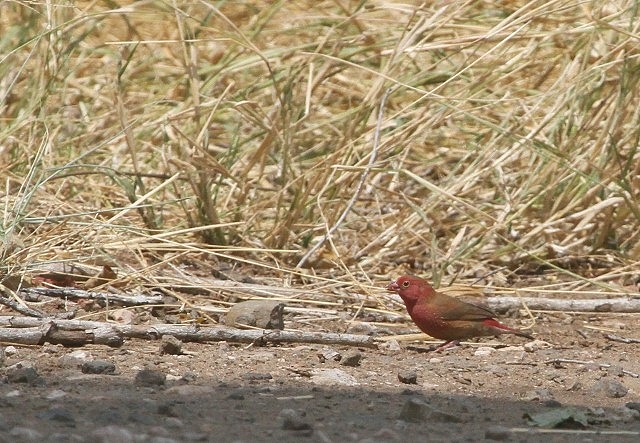
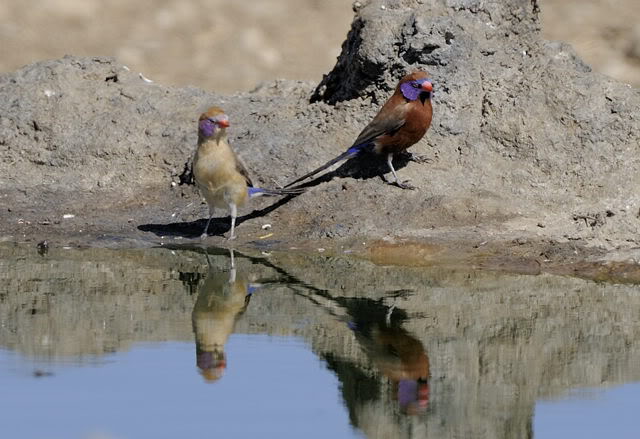
The adult male has scarlet plumage and brown wings and an almost entirely red head and breast. Red is most extensive on forehead and hind neck. Lower belly and undertail coverts deep buff/rose red. Sides of the breast spotted with small white spots to varying degrees.
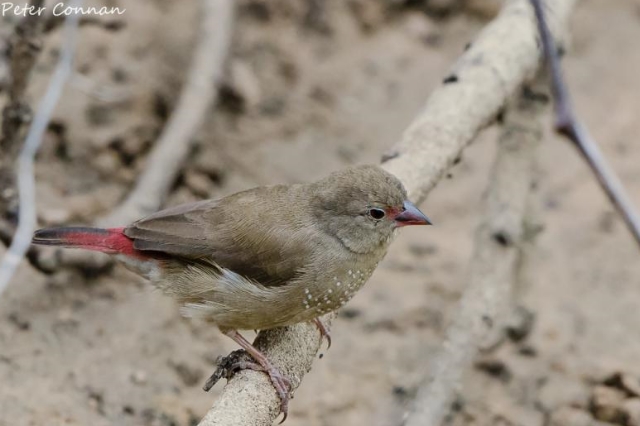
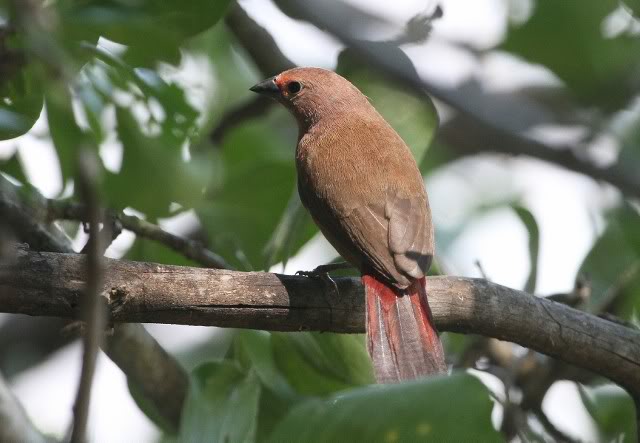
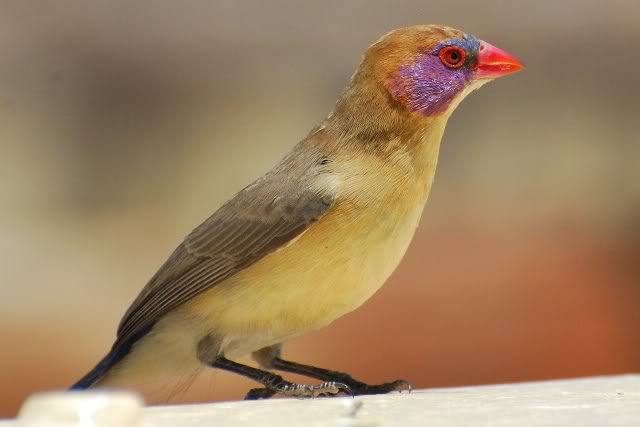
The female is much duller, with only the lores, rump and upper tail pink, and is otherwise sandy brown. Red stripe from base of lower mandible to, and sometimes over, the eye. White spots on the breast larger and usually more profuse than on the male.
The juvenile resembles the female but lacks the yellow eye-ring, the pink lores and white spots. It has an entirely black bill.
Similar species: Brown Firefinch is much more dusky and has a brown (not pinkish-red) rump. Male has red confined to upper breast and face; female red only on throat and lores. Juv Red-billed Firefinch frequently mistaken for Brown Firefinch because dull reddish rump often hard to see in poor light. Jameson's and African Firefinches have black (not red) bills; males with lower bellies and undertails black (not deep buff). African Firefinch male has mostly grey (not pinkish-red) head; female has underparts pinkish buff (not buff).
Distribution
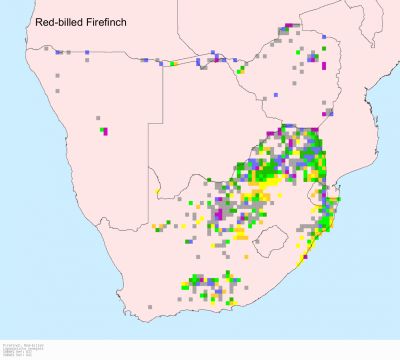
It occurs across much of sub-Saharan Africa, excluding the Lowland forest in and around the DRC, from Senegal to Somalia south to southern Africa. Here it is common from Zimbabwe and Mozambique west to northern Botswana and Namibia and south to north-eastern and northern South Africa, while more scarce in the Northern, Eastern and Western Cape.
Habitat
It generally prefers rank grass and thickets with patches of bare soil, especially in moist woodland and Acacia savanna, also occupying cultivated fields and thickets near water.
Diet
It mainly eats grass seeds taken from the ground, supplemented with insects, often joining mixed-species foraging flocks along with other seedeaters.
Breeding
Monogamous. The nest is built solely by the male, consisting of a ball-shaped structure with a side entrance, made of dry grass blades with an inner shell of grass inflorescences, lined with feathers. It is typically placed in plant debris beneath a tree or bush, alternatively in a thatch roof, hedge or hole in a wall. Egg-laying season is almost year-round, peaking from December-June. It lays 2-6 eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for about 11-12 days. The chicks are fed by both parents, leaving the nest after about 17-20 days and becoming fully independent approximately 2-4 weeks later.
Parasitised by Village Indigobird.
Call
A sharp, fast vut-vut-vut-chit-chit and a sweep. Listen to Bird Call.
Status
Common resident, sedentary but with some localised movements.



 © Peter Connan
© Peter Connan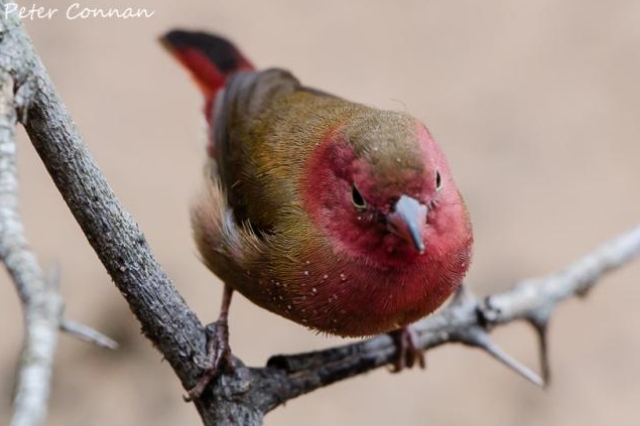 © Peter Connan
© Peter Connan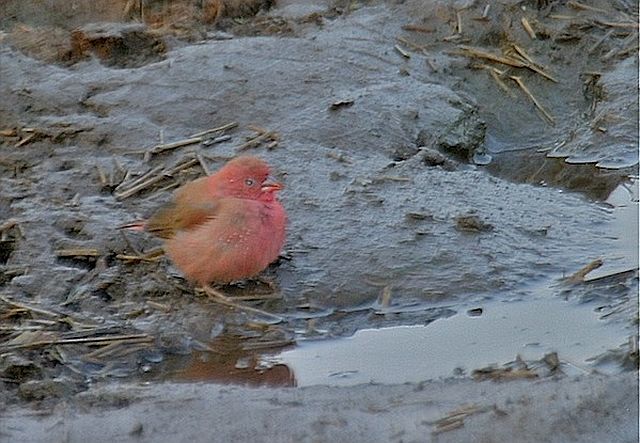 © ExFmem
© ExFmem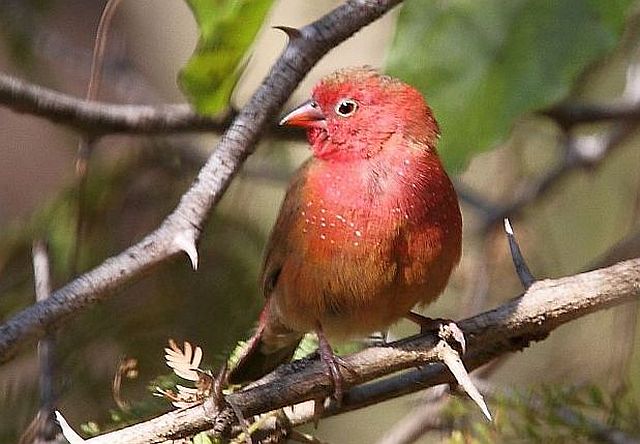 © Sharifa
© Sharifa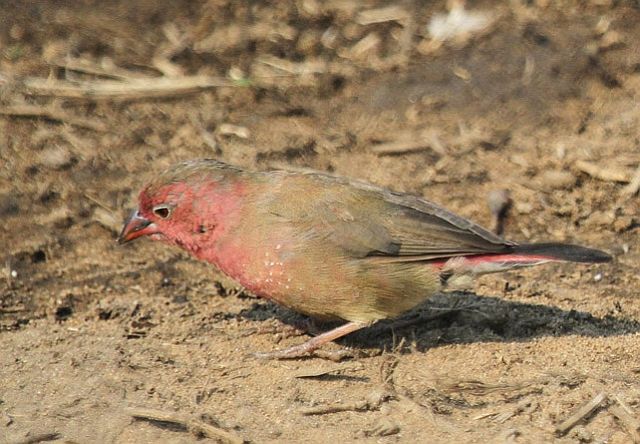 © leachy
© leachy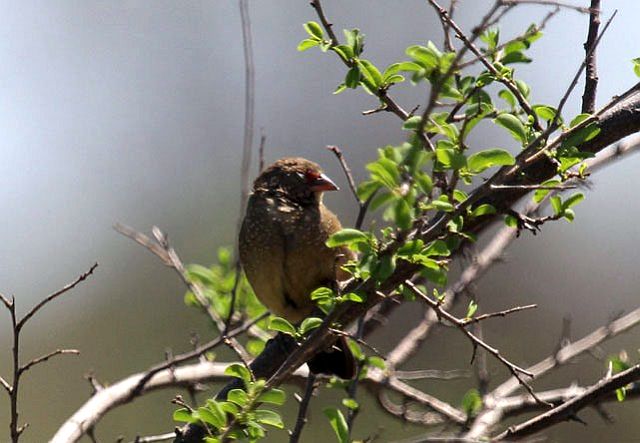 © leachy
© leachy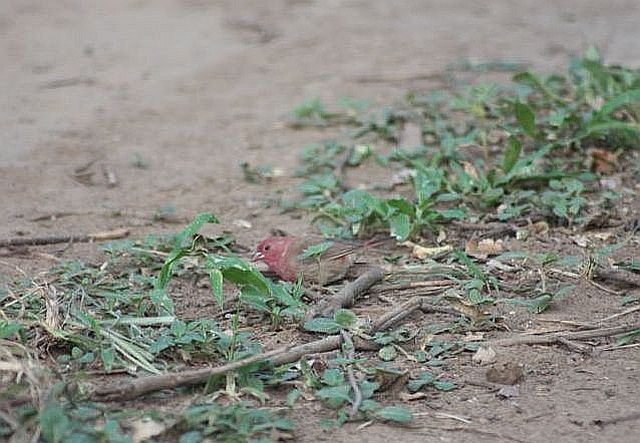 © harrys
© harrys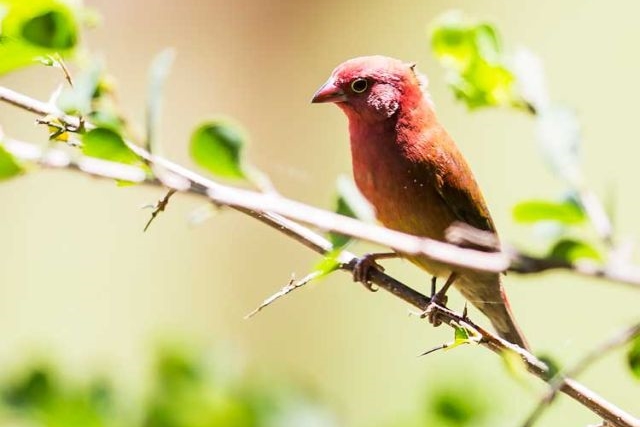 © Pumbaa
© Pumbaa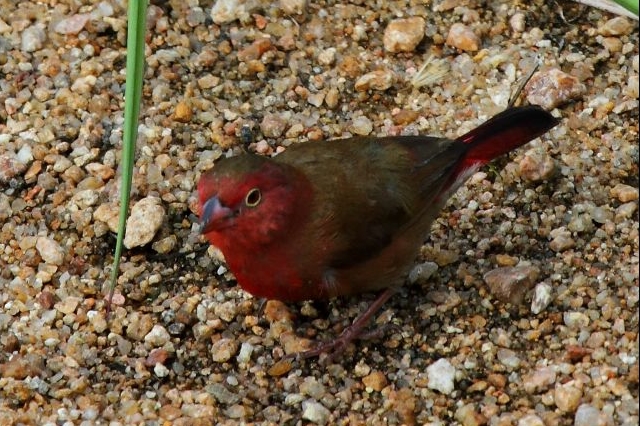 © Duke
© Duke
 © ExFmem
© ExFmem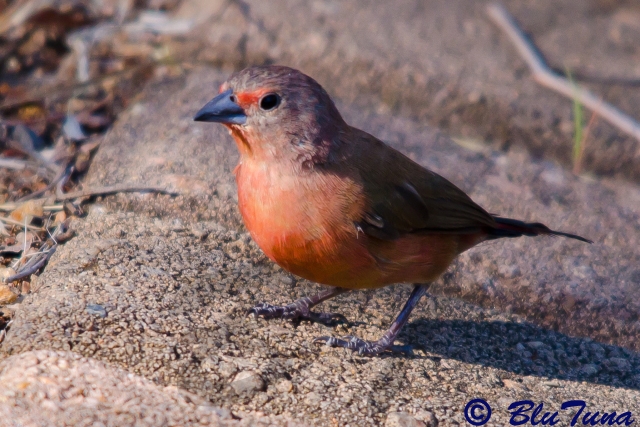 © BluTuna
© BluTuna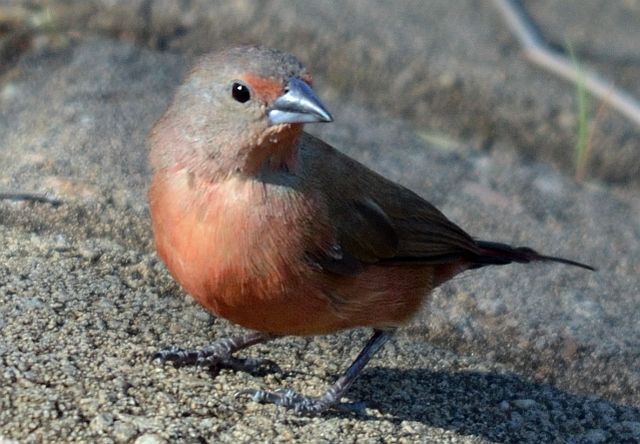 © BluTuna
© BluTuna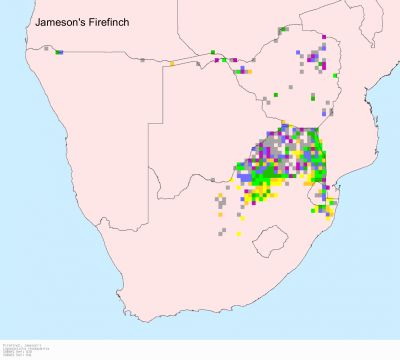
 © nan
© nan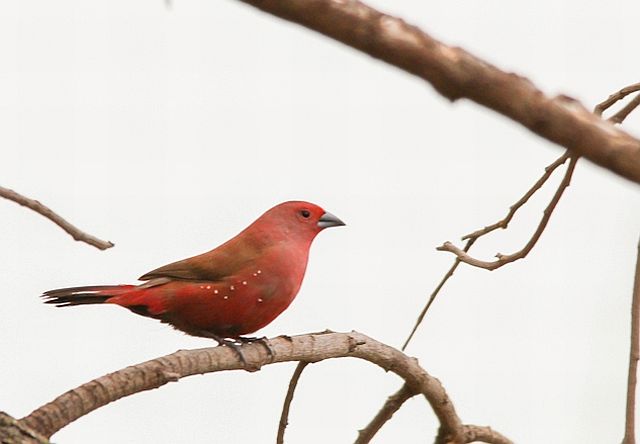 © Super Mongoose
© Super Mongoose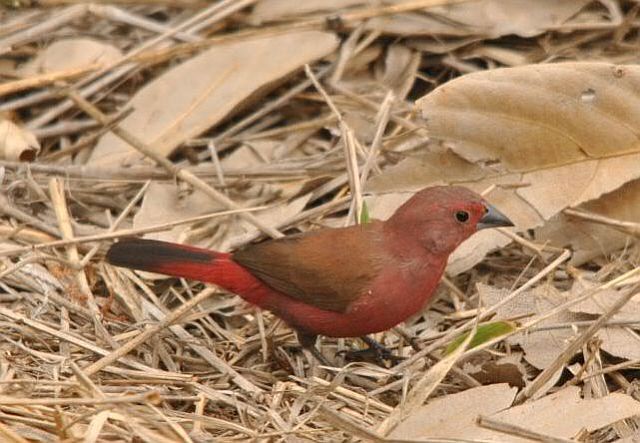 © lowveldboy
© lowveldboy © JustN@ture
© JustN@ture © Amoli
© Amoli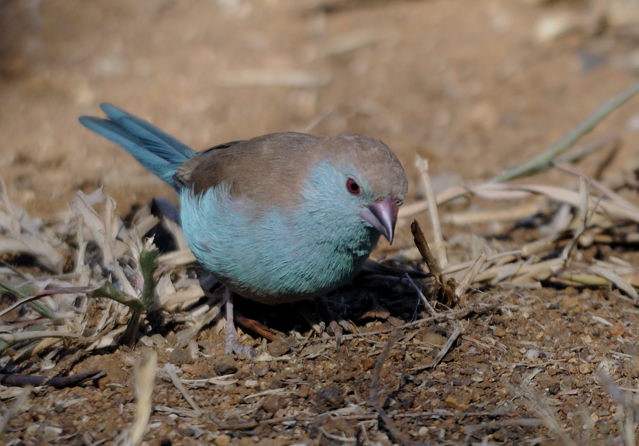 © Dewi
© Dewi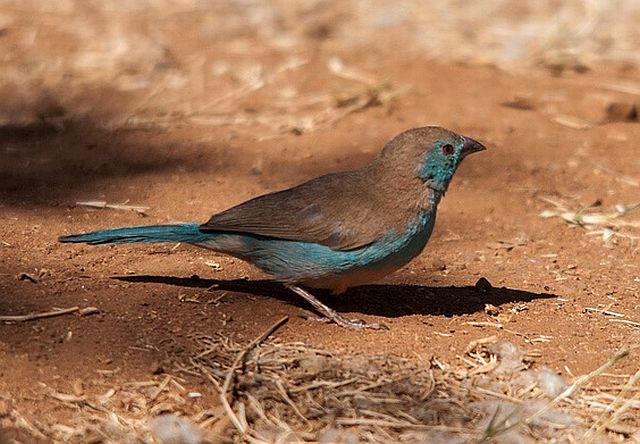 © Joan
© Joan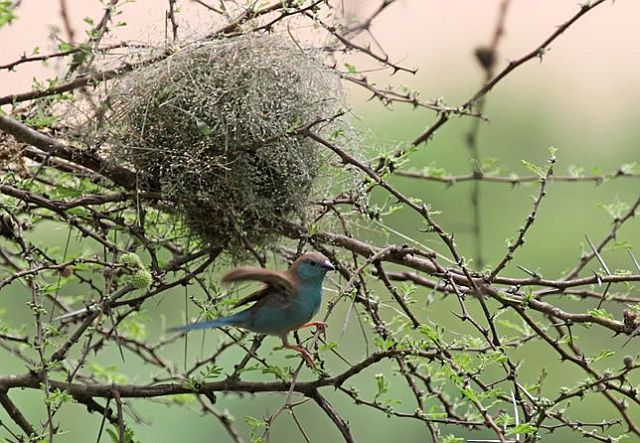 © leachy
© leachy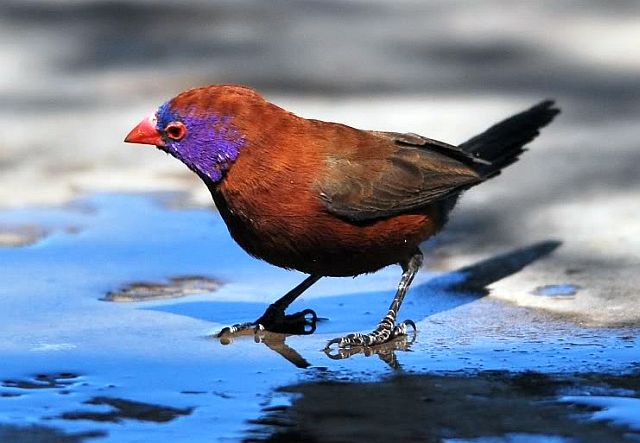
 © Dewi
© Dewi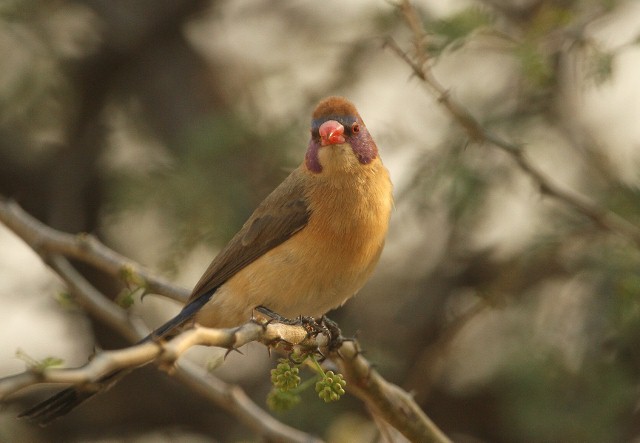 © nan
© nan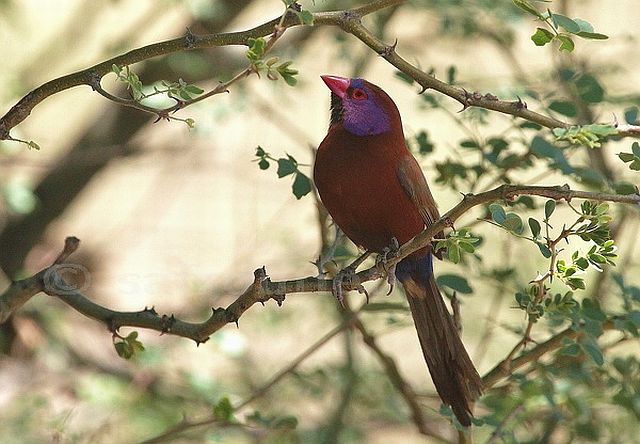 © nan
© nan