Order: Piciformes. Family: Indicatoridae
Description
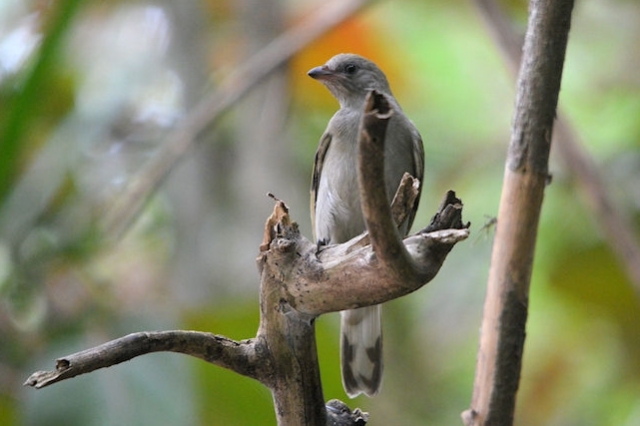
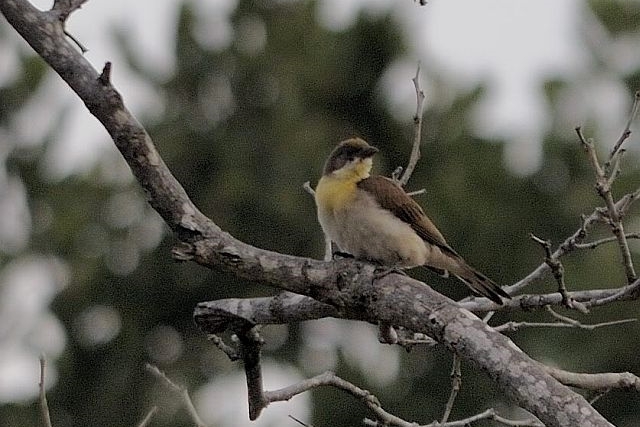
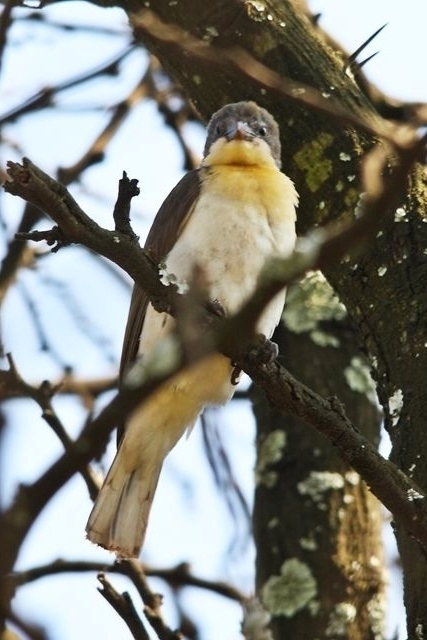
Size smallish (smaller than Greater and Scaly-throated Honeyguides) 15-16 cm; head and breast grey, shading to white on belly; back olive grey with gold wash; tail dark, outer rectrices white (conspicuous in flight); malar stripe blackish. Iris dark brown; bill blackish horn, base pinkish; legs and feet olive grey.
Juvenile: Darker below than adult; tail feathers pointed, outermost more extensively white.
Distribution
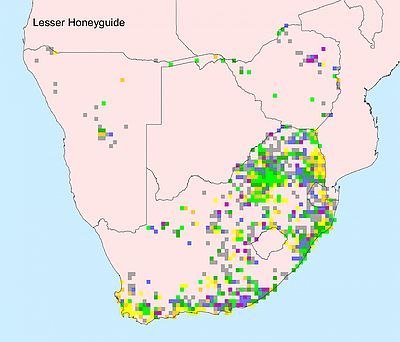
Occurs across much of sub-Saharan Africa, excluding dense forest and arid areas. In southern Africa, it is absent from large areas of Botswana, Mozambique and Namibia.
Taxonomy
Indicator minor has 6 subspecies:
I. m. minor South Africa, south-eastern Botswana, Swaziland;
I. m. senegalensis Senegal, Chad, Cameroon, Sudan;
I. m. riggenbachi Cameroon, Sudan, Uganda;
I. m. diadematus Sudan, Ethiopia, Somalia;
I. m. damarensis Angola, Namibia;
I. m. teitensis Democratic Rep. of Congo, Angola, Kenya, Uganda, Mozambique, Zimbabwe and lowlands of eastern South Africa.
Habitat
It generally prefers woodland, savanna, riverine forest, forest edges, plantations and gardens.
Diet
It feeds on a wide variety of insects, as well as a number of products and adults of Apis mellifera (Honey bee). Unlike other honeyguides, it does not lead mammals to bees nests. It feeds on insects in crevices, bark, leaves and branches, and is also highly adept at finding dry honeycombs.
Breeding
It is a brood parasite, meaning that it lays its eggs in other bird nests, which are usually other hole & cavity nesters such as Barbets & Bee-eaters. The host, thinking that the egg is its own, incubates the egg, and cares for the chick. It is also polygynous, as it may have multiple mates at the same time. Egg-laying season from August-February, peaking from October-November. The parasitising process involves either the breeding pair or just the female. If there are both, the male distracts the host bird while the female rushes into the nest, laying one egg before the pair leave. If it is just the female, she simply lays its egg while the host bird is out. The eggs are laid in series of 2-7, each in a different nest, laying about 18-20 eggs in the whole breeding season. Soon after the chick hatches it viciously kills the host birds chicks, with extraordinary strength. It stays in the nest for about 37-38 days before becoming independent.
Call
Series of 10-30 far-carrying piping unmusical ki-link ki-link ki-link notes; pauses about half minute between series; each series starts with sharp tweet or kew note; display flight in undulating circles accompanied by single whurrr, probably made by tail feathers.
Status
Common resident.


 © 100ponder
© 100ponder
 © Dewi
© Dewi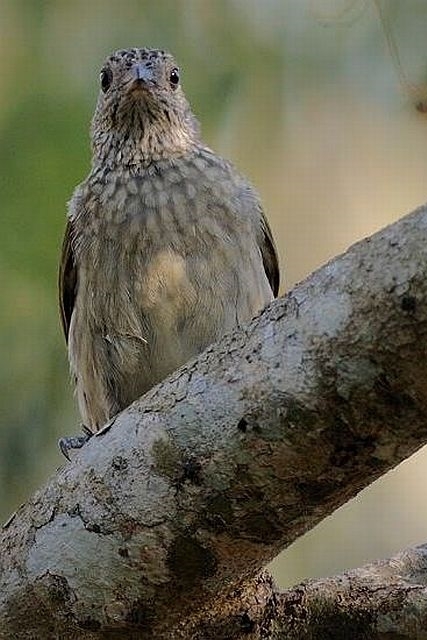 © Dewi
© Dewi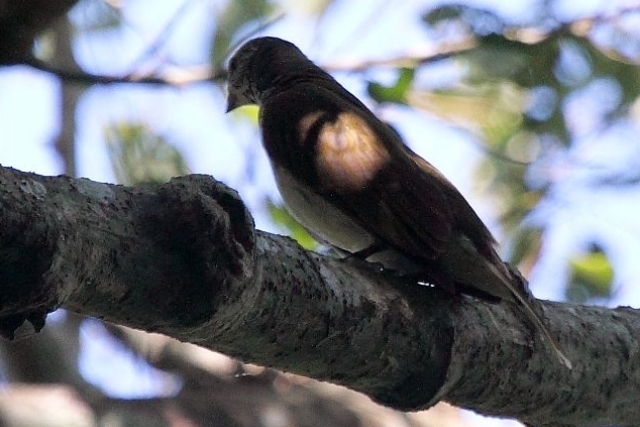 © Duke
© Duke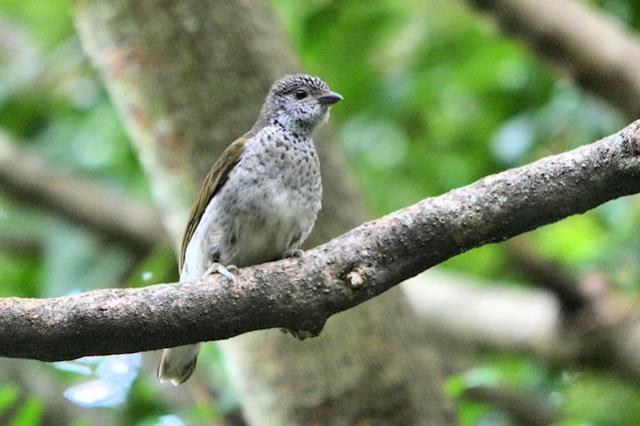 © 100ponder
© 100ponder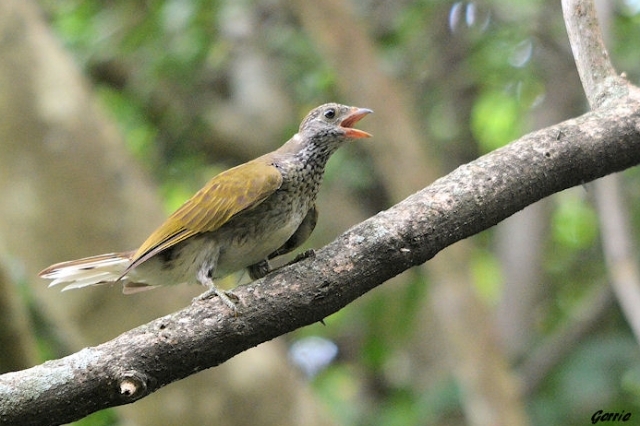 © 100ponder
© 100ponder
 © Flutterby
© Flutterby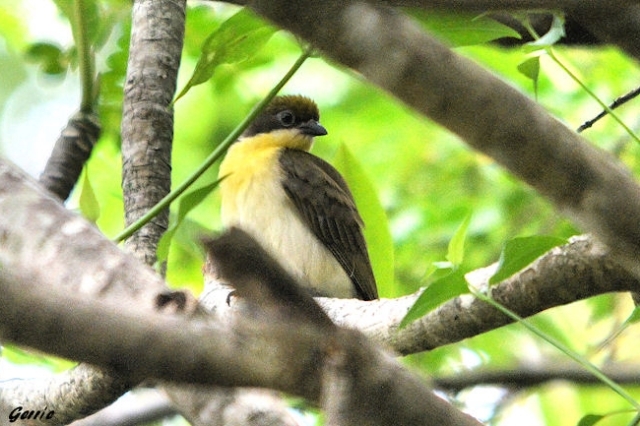 © 100ponder
© 100ponder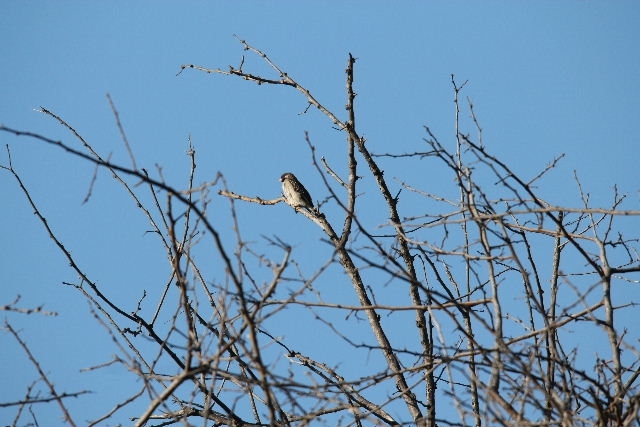 © pooky
© pooky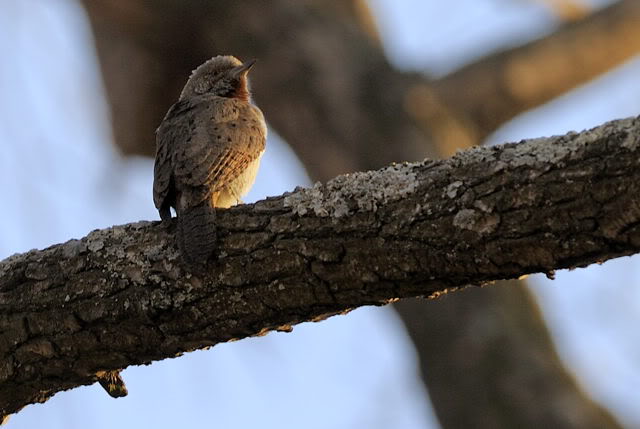 © Dewi
© Dewi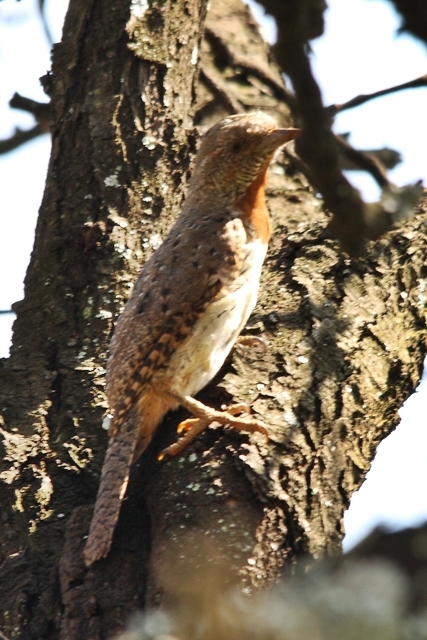 © Flutterby
© Flutterby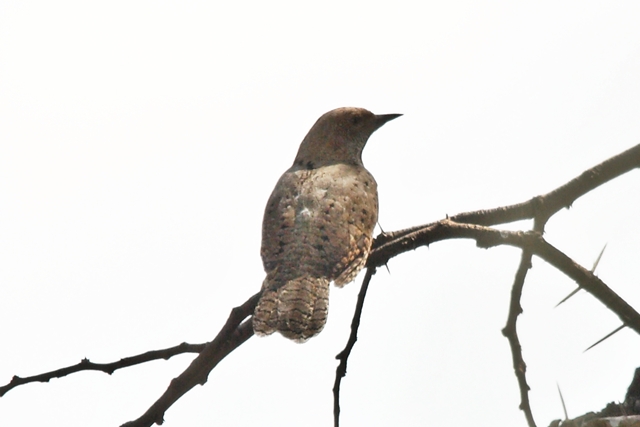 © Flutterby
© Flutterby